“The endogenous cannabinoid system, named after the plant that led to its discovery, is perhaps the most important physiologic system involved in establishing and maintaining human health.”
It’s becoming increasingly clear that stimulating and supporting your endocannabinoid system is another way to improve your brain and mental health.
But you don’t need to smoke marijuana to do this.
There are a number of other options, and this article explore them.
But first, what exactly is your endocannabinoid system?
Well, your body actually creates its own cannabinoids, similar to those found in cannabis.
And these naturally-occurring cannabinoids bind to cannabinoid receptors within your body and brain.
You can think of these receptors like little “locks”, and your body’s cannabinoids fit naturally into these locks like “keys”. Together, they make up your endocannabinoid system, which can influence your appetite, pain, inflammation, sleep, stress responses, mood, memory, motivation, reward, etc. (91-92).
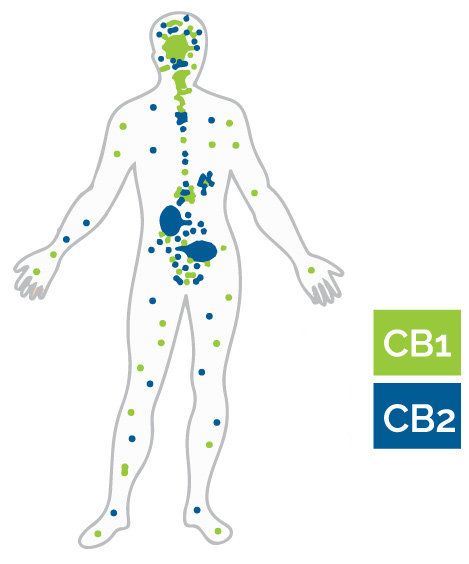
There are two main cannabinoid receptors – cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2).
CB1 receptors are mostly found in the brain and impact a number of neurotransmitters, including GABA, glutamate, dopamine and serotonin. CB2 receptors, on the other hand, are mostly found within the immune system and blood cells (93-99).
However, it’s important to note that some CB1 receptors are still located outside the brain, and some CB2 receptors can be found within the brain. So, there is some overlap.
According to Martin Lee, author of Smoke Signals: A Social History of Marijuana, cannabinoid receptors are more abundant in the brain than any other type of neurotransmitter receptor.
There are two different types of cannabinoids that can activate these receptors in your body:
Phytocannabinoids – plant-derived cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) found in marijuana
Endocannabinoids – as mentioned before, these cannabinoids are produced naturally within the body. Anandamide is the main endocannabinoid in your body. It can be found in humans, but also many other animals and plants. It binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors and has similar effects as THC. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is another critical endocannabinoid in your body that also binds to the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Its effects are similar to CBD (100-107).
What Are the Benefits of Stimulating and Supporting Your Endocannabinoid System?
“Modulating the activity of the endocannabinoid system has turned out to hold therapeutic promise in a wide range of disparate diseases and pathological conditions, ranging from mood and anxiety disorders, movement disorders such as Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease, neuropathic pain, multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injury, to cancer, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, stroke, hypertension, glaucoma, obesity/metabolic syndrome, and osteoporosis, to name just a few.”
There is an increasing amount of research linking a number of illnesses and symptoms to low endocannabinoids levels, including:
Major depression (136-139)
Generalized anxiety disorder (140-141)
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (142-144)
Multiple sclerosis (145-148)
Sleep disorders (150-152)
Fibromyalgia (153)
Parkinson's (154)
Some researchers are convinced that when your body doesn’t produce enough endocannabinoids (anandamide and 2-AG), you’re more likely to develop these diseases.
They’ve even coined the term “Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency” to describe the problem (108).
But if you have one of the above conditions, don’t worry!
You can stimulate and support your endocannabinoid system naturally, which can lead to a number of brain and mental health benefits:
Less stress and anxiety (109-110)
Improved mood and increased feelings of pleasure and optimism (111-114)
Better focus and concentration (115)
Less hyperactivity and impulsivity (116)
Higher BDNF levels (117-118)
Increased rate of neurogenesis (119-122)
Increased myelin formation (123-126)
Deeper sleep (127-129)
Lower cortisol levels (130-131)
Fewer headaches and migraines (132)
Reduced activity in the amygdala, the fear centre of the brain (133-134)
Reduced inflammation (135)
So without further ado, here are 26 ways to stimulate and support your endocannabinoid system naturally.
1. Cold Exposure
Cold exposure has been shown to increase endocannabinoid levels (1).
Researchers have also found that cold exposure significantly increases the density of CB1 neurons (2).
To support my endocannabinoid system, I take a cold shower every day, and often go outside with minimal clothing in the winter.
Try finishing your next shower with at least 30 seconds of cold water and see how you feel.
Then work your way up to longer periods of time.
It's painful to do, but the lingering effects are worth it.
You can also ease yourself into it by simply sticking your face in ice cold water.
Cold exposure also stimulates the vagus nerve.
2. Sex Hormones
Male and female sex hormones also stimulate and support the endocannabinoid system.
Both testosterone and estradiol have been shown to upregulate CB1 receptors (3-4).
Estradiol also increases the synthesis and release of the endocannabinoids (anandamide), which activates CB1 receptors (5-6).
And the plasma levels of anandamide correlate nicely with the levels of estrogen during the menstrual cycle in women (7).
I recommend both men and women get their hormones checked regularly.
You can get your testosterone levels checked here and your estradiol levels checked here.
I used to have low testosterone and testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) really improved my brain and mental health when I used to take it.
3. Coffee
Drinking coffee is another way to stimulate and support your endocannabinoid system.
Researchers believe that the cannabinoid system is involved in the psychoactive properties of caffeine (10).
Regular caffeine consumption has been shown to enhance the activation of CB1 receptors by endocannabinoids (8).
CB1 receptors are downregulated after “social defeat stress”, but caffeine counteracts this effect (9).
I drink one cup of coffee most mornings.
Coffee and caffeine can disrupt sleep though, so make sure you don’t drink it later in the day. I have my last cup sometime between 10 in the morning and noon. If I have it any later than that, it disrupts my sleep.
It's also a good idea to try to consume the whole coffee fruit, instead of just the coffee bean or pure caffeine.
Traditionally, the coffee bean is extracted from the coffee fruit for roasting. And the surrounding fruit is discarded.
But that’s a huge problem.
Because the coffee fruit contains several healthy compounds not found in coffee beans themselves.
And after years of careful clinical research, scientists have discovered that ingesting whole coffee fruit concentrate significantly increases brain function.
Coffee fruit concentrate is included in the Optimal Brain supplement.
4. Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Olive oil has numerous health benefits, particularly because of its strong anti-inflammatory effects.
It’s also been shown to upregulate CB1 receptors (11).
I add olive oil to my salads and sometimes even just take a tablespoon of it straight.
Be careful though. A lot of the cheap extra virgin olive oils in grocery stores are not actually “extra virgin.”
Investigations have found that there is a lot of fraud within the olive oil industry and many so-called extra virgin olive oils contains other cheaper, refined vegetable oils, such as soybean, corn and canola.
This is discussed more in the book Extra Virginity: The Sublime and Scandalous World of Olive Oil.
5. Cannabidiol (CBD) Oil
Cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the active cannabinoids in cannabis.
It is not psychoactive but it has a wide range of medical applications.
Research shows that CBD enhances the expression of CB1 receptors in the brain (12-13).
It also increases levels of 2-AG by preventing it from breaking down (14-15).
I used to take CBD oil but no longer need to take it.
It reduced my stress, made me really sleepy and knocked me out before bed.
6. Flavonoids
Flavonoids are a diverse group of plant compounds found in almost all fruits and vegetables.
Chocolate, tea, wine, and some beans, herbs, spices, nuts and seeds contain them. Overall, the more colorful a food is, the richer it is in flavonoids.
The following flavonoids inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which is the enzyme responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids (anandamide) (16):
Genistein
Kaempferol
7-hydroxyflavone
3,7-dihydroxyflavone
I try to eat as many fruits and vegetables as possible on a daily basis so that I’m consuming plenty of flavonoids.
It’s best to consume fruits and vegetables in their raw forms to receive the highest number of flavonoids (cooked fruits and vegetables have less).
Check out my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain Health for a bunch of flavonoid-rich foods.
7. Tea
Tea contains catechins, which are antioxidant compounds that have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.
Researchers have found that catechins in tea target and bind to cannabinoid receptors in the central nervous system (25-26).
Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is the most well known catechin. It’s found in green tea. I take a concentrated green tea extract with EGCG to support my endocannabinoid system.
Drinking tea can also lower cortisol, and green tea increases BDNF.
8. Kava
Kava is a plant located in the western Pacific. The root of the plant is used medicinally to treat anxiety and sleep disorders because it causes relaxation without impacting cognitive performance. Some people say it feels like drinking alcohol (30-31).
Researchers have evaluated commercially available kava supplements to see whether they bind to cannabinoid receptors. They found that yangonin, a compound in kava, binds to the CB1 receptor, and concluded that kava’s anti-anxiety effects may be because it stimulates the endocannabinoid system (32).
I searched for kava supplements that include yangonin and found this one.
I personally don’t take kava anymore because I get a weird reaction from it and I found out I’m allergic to the plant.
9. Osteopathy
Osteopathy is a healing modality that emphasizes the treatment of disease by manipulating and massaging the bones, joints, and muscles.
One study found that endocannabinoid levels increased by 168% on average after osteopathic treatment. (33).
Practitioners of osteopathy are referred to as osteopaths. I saw an osteopath in Ottawa soon after my concussions in 2010. I had been suffering from constant dizziness, and his therapy completely reversed the dizziness. And it was permanent. The dizziness never came back. I was amazed and very grateful.
I recommend finding an osteopath in your area if you’ve ever suffered a traumatic brain injury.
If you happen to be in the Ottawa area, go to the one that I did.
10. Probiotics
Research suggests that some probiotics can stimulate and support the endocannabinoid system.
In one study, researchers found that lactobacillus acidophilus, a specific probiotic species, increases the expression of CB2 receptors (53).
Lactobacillus acidophilus is included in the Optimal Biotics supplement.
Probiotics have also been shown to stimulate the vagus nerve and help with depression.
And here are five other ways to increase the good bacteria in your gut.
11. Dark Chocolate
Most people know dark chocolate is rich in multiple antioxidants, such as flavonols and polyphenols, which reduce oxidative stress.
But interestingly, it also contains the endocannabinoid anandamide (54).
Dark chocolate also other compounds that slow down the breakdown of anandamide, increasing the amount of anandamide that stimulates your endocannabinoid system (55-56).
This is likely one reason why eating chocolate makes people feel so good.
Dark chocolate also increases BDNF and reduces cortisol.
12. Reduce Stress
I highly recommend you try to do something every day to manage your stress because emotional stress has been shown to downregulate CB1 receptors (57-58).
High cortisol levels for prolonged periods of time, such as those caused by chronically stressful circumstances, also reduces CB1 receptors and significantly reduces cannabinoid binding to CB1 receptors (59-62).
On top of this, chronic psychological stress reduces endocannabinoid levels in the brain (63-66).
Overall, researchers say there is strong evidence that the endocannabinoid system needs to function optimally in order to properly deal with stress (67).
Some of my favourite ways to reduce stress include neurofeedback, meditation (using the Muse headband), massage, acupuncture, eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), emotional freedom techniques (EFT), heart-rate variability (HRV) training, and using an acupressure mat.
Some supplements that can help you reduce stress include zinc, magnesium, ashwagandha and phosphatidylserine.
This anti-anxiety supplement also includes a number of natural compounds that have personally helped me manage my stress over the years.
And here is an article with 20 other ways to lower your stress hormone, cortisol.
13. Magnolia Officinalis
Magnolia Officinalis is a plant that has neuroprotective properties and relaxing effects.
It’s used in Chinese traditional medicine for the treatment of anxiety, depression and sleeping disorders.
Researchers have found that Magnolia officinalis extract and its main bioactive constituents, magnolol and honokiol, can activate cannabinoid receptors (17).
You can either supplement with an extract, or you can drink Magnolia tea.
Both the tea and extract should be taken with a meal consuming fat because the active ingredients are fat soluble.
14. Exercise
Exercise is another great way to stimulate and support your endocannabinoid system.
Medium and high-intensity exercise has been shown to activate the endocannabinoid system (73).
Research also shows that exercise significantly upregulates CB1 receptors and enhances CB1 receptor sensitivity, which is why exercise can protect against the consequences of stress (68, 72, 74).
Exercise-related improvements in memory are also due to activation of the CB1 receptor. Blocking this receptor seems to prevent the memory benefits of exercise (69, 72).
Several studies also show that exercise increases levels of anandamide and activates cannabinoid signaling (70-71).
And researchers now believe that endocannabinoids may actually be responsible for the “runner’s high” (euphoria) that you get when you exercise, and not endorphins (76-77).
However, you shouldn’t force yourself to exercise. Forced exercise is seen by the endocannabinoid system as a type of stress, and therefore doesn’t increase endocannabinoid levels and can actually decrease CB1 signaling (75).
So, you should find an aerobic activity that you enjoy so that it’s not a burden.
This is exercise routine I try to follow consistently:
Lift heavy weights 1-4 times per week
High-intensity interval sprinting 1-2 times per week
Walk as much as I can (ideally 30-60 minutes every day)
Run for 20-30 minutes before lifting weights
15. Palmitoylethanolamide
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) is a natural compound that has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, and low levels of PEA can contribute to chronic brain inflammation and pain (20).
Research shows that PEA can alleviate pain and increase mood by enhancing endocannabinoid activity (18-19, 21-24).
PEA is naturally found within the body, but it’s also available as a supplement. It's even used for medical purposes in Italy and Spain.
16. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that your body cannot produce itself. They are necessary for the normal electrical functioning of your brain and nervous system.
Research shows that they increase the synthesis of endocannabinoids and upregulate both CB1 and CB2 receptors (78-79).
There is also a connection between low omega-3 fatty acid intake, poor endocannabinoid function and mood changes (80).
Omega-3 fatty acids are found primarily in cold water fish such as salmon, black cod, sablefish, sardines and herring.
Unfortunately, most people don't consume enough omega-3 fatty acids through their diet.
That’s why I recommend people supplement with krill oil, a special kind of fish oil that contains the essential omega-3 fatty acids.
And you can read more about the importance of omega-3 fatty acids here.
17. Agmatine
Agmatine is a metabolite of the amino acid arginine.
It can help reduce pain, treat drug addiction, and protect the brain from toxins (27-28).
It has been shown to enhance the painkilling effects of cannabinoids. It does this by increasing cannabinoid action and signalling through the CB1 receptor (29).
My personal experience with agmatine is that it made me agitated, so I stopped taking it. But I don’t have any symptoms of pain. If you do, I think it’s worth trying.
18. Caryophyllene
Caryophyllene is a compound found in many plants and essential oils, including clove, rosemary, basil, oregano, lavender, and hops. It also contributes to the spiciness of black pepper (34).
Caryophyllene has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, antidepressant, anti-anxiety and anti-alcoholism effects (35, 40-41).
These effects are likely because it binds to the cannabinoid receptors (36-37, 39, 42-43).
It can also help reduce neuropathic pain through the CB2 receptor (38).
19. Echinacea
Echinacea is a Native American medicinal plant and one of the most popular medicinal herbs.
People often use it to reduce flu symptoms and shorten the duration of the common cold. It’s also sometimes used to reduce anxiety and relieve fatigue.
Compounds in Echinacea, called alkylamides, have been shown to reduce inflammation by binding to the CB2 receptor (44, 46-47).
Researchers have also found that alkylamides increase the effect of endocannabinoids (45).
20. Black Truffle
Tuber melanosporum, also called the black truffle, is an edible mushroom native to Southern Europe.
Researchers have found that black truffles contain the endocannabinoid anandamide (49).
Black truffle peelings can be added meals and go particularly well with mashed potatoes.
21. Diindolylmethane (DIM)
Diindolylmethane (DIM) is an anti-carcinogenic compound found in cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, cabbage and kale.
DIM is one of the reasons why these foods are considered so healthy.
Studies show that DIM reduces inflammation because it binds to CB2 receptors (50-51).
You can also take it as a supplement.
22. Ruta Graveolens
Ruta graveolens, commonly known as rue, is a medicinal herb.
Researchers have found that a compound within it binds to cannabinoid receptors (52).
Rue can be taken as an extract.
23. Acmella Oleracea
Acmella Oleracea, also known as Electric Daisy, is a medicinal herb originating from the Amazon region.
It contains phytocannabinoids and other compounds that can reduce pain and inflammation (81-82).
It’s available as an extract.
24. Helichrysum Umbraculigerum
Helichrysum Umbraculigerum is a plant with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, originating from South Africa.
It’s been used medicinally for thousands of years, especially in countries like Italy, Spain, and Portugal.
Researchers have found that it has antidepressant effects likely because it contains cannabigerol, a phytocannabinoid that stimulates the endocannabinoid system (83-85).
A number of different essential oils with Helichrysum Umbraculigerum are available.
25. Radula Marginata
Radula Marginata is a plant commonly found in New Zealand.
It contains cannabinoids and cannabinoid-like compounds that bind to CB1 receptors, activating the endocannabinoid system (86-90).
26. Curcumin
Curcumin is the most heavily researched compound within turmeric, the spice that gives curry its yellow colour.
Researchers have found that supplementing with curcumin for 4 weeks reduces depression by binding to the CB1 receptor and increasing endocannabinoid levels in the brain (155).
Curcumin is included in the Optimal Energy supplement.
Since curcumin is a fat soluble, take it with a fatty meal.
Conclusion
As you can see, there are many different ways to stimulate your endocannabinoid system besides smoking cannabis.
And supporting this important system can lead to a number of brain and mental health benefits.
I hope you implement some of these strategies into your regular routine and notice you feel better and live more optimally over time.
If you think you know someone who might benefit from this article, please share it with them.
Enjoy This Article? You Might Also Like My FREE Food Guide for Optimal Brain and Mental Health!
References:
(1) http://www.jlr.org/content/57/3/464.short
(3) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24055403
(4) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21412772
(5) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3697880/
(6) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12393387/
(7) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21227997
(8) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19027757
(9) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19027757
(10) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19027757
(11) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25533906
(12) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18021759
(13) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016561470900128X
(14) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4301686/
(15) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.go
(16) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2931553/
(17) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24900561
(18) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1621151/
(19) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2597234/
(20) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palmitoylethanolamide
(21) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9685157
(22) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11426841
(23) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8739213
(24) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21857095
(25) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19897346
(26) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2931553/
(27) https://examine.com/supplements/agmatine/
(28) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agmatine
(29) https://wwwhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19538988ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19538988
(30) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kava
(31) http://www.umm.edu/health/medical/altmed/herb/kava-kava
(32) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nihttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22525682.gov/pubmed/22525682
(33) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16118355
(35) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caryophyllene
(36) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caryophyllene
(37) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2931553/
(38) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2931553/
(39) http://www.pnas.org/content/105/26/9099.long
(40) http://www.europeanneuropsychopharmacology.com/article/S0924-977X(13)00302-7/abstract
(41) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031938414003400
(42) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2449371/
(43) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18574142
(44) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2931553/
(45) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2931553/
(46) http://www.jbc.org/content/281/20/14192.full.pdf
(47) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16142631
(48) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031942214004956
(49) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031942214004956
(50) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2931553/
(51) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19286662/
(52) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19096995/
(53) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17159985
(54) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8751435
(55) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2931553/
(56) www.sacredchocolate.com/docs/sacredpdf/brain-cannabinoids-chocolate.pdf
(57) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/febs.12125/full#febs12125-bib-0082
(58) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19027757
(59) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3706194/
(60) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18058925/
(61) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3706194/
(62) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21263035/
(63) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3706194/
(64) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20439721/
(65) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20348201
(66) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(67) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(68) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3055381/
(69) http://www.leafsciencehttp://
(70) http://www.leafscience.com/2013/11/04/study-memory-benefits-exercise-tied-cannabinoid-system/
(71) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hipo.22206/abstract
(72) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hipo.22206/abstract
(73) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14625449
(74) http://www.os-extra.cannabisclinicians.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/ECSSCC-listing.pdf
(75) http://www.os-extra.cannabisclinicians.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/ECSSCC-listing.pdf
(76) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26438875
(77) http://www.os-extra.cannabisclinicians.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/ECSSCC-listing.pdf
(78) http://docs.lib.purdue.edu/dissertations/AAI3444794/
(79) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21278728
(80) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21278728
(81) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabinoid
(82) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18289087
(83) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabinoid
(84) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18289087
(85) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0031942279830253
(86) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radula_marginata
(87) http://cpb.pharm.or.jp/cpb/200210/c10_1390.pdf
(88) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12372871
(89) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cannabinoid
(90) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18289087
(91) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23008748
(92) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27554802
(93) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2241751/
(94) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(95) http://www.nature.com/cdd/journal/v22/n10/full/cdd201511a.html
(96) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21749363
(97) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2165569
(98) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1718258
(99) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21295074
(100) http://www.leafscience.com/2013/11/04/study-memory-benefits-exercise-tied-cannabinoid-system/
(101) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anandamide
(102) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9285589
(103) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9915812
(104) http://www.nature.com/cdd/journal/v22/n10/full/cdd201511a.html
(105) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21749363
(106) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8751435
(107) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9285589
(108) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18404144
(109) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(110) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(111) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(112) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(113) http://thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(10)60935-X/fulltext
(114) http://www.nel.edu/pdf_/25_12/NEL251204R02_Russo_.pdf
(115) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(116) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(117) http://www.leafscience.com/2013/11/04/study-memory-benefits-exercise-tied-cannabinoid-system/
(118) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(119) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16224541
(120) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16037095
(121) http://www.jci.org/articles/view/25509
(122) http://www.leafscience.com/2013/11/04/study-memory-benefits-exercise-tied-cannabinoid-system/
(123) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15044630
(124) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21480865
(125) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10716447
(126) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11156943
(127) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8569415
(128) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9813364
(129) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(130) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(131) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(132) http://www.
(133) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(134) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(135) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22265864
(136) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(137) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(138) http://thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(10)60935-X/fulltext
(139) http://www.nel.edu/pdf_/25_12/NEL251204R02_Russo_.pdf
(140) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(141) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(142) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(143) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3817535/
(144) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(145) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15044630
(146) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21480865
(147) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10716447
(148) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11156943
(149) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(150) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8569415
(151) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9813364
(152) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2685476/
(153) http://www.nel.edu/pdf_/25_12/NEL251204R02_Russo_.pdf
(154) http://www.nel.edu/pdf_/25_12/NEL251204R02_Russo_.pdf