Being depressed doesn’t mean you’re weak.
It’s not a defect in your personality.
As I’m sure you know, it’s often caused by physiological changes in your body and brain.
So you need to think of it like any other illness.
If you have a broken bone, you need to wear a cast to stabilize the bone while it heals.
And if you have depression, you need to be kind to yourself, as you seek and address the underlying root causes.
The good news is that you’re not powerless.
I used to think that I’d be depressed forever.
That my depression was simply genetic, and I couldn’t do anything about it.
In fact, I accepted that notion for a while.
I felt defeated and hopeless, and thought I'd feel that way for my entire life.
I told myself I’d simply have to rely on drugs to survive because that’s just “how I’m wired”.
But then one day, I changed my mind and decided that I’d had enough.
And I was actually going to get to the bottom of it instead of just accepting it.
I took action and searched far and wide for safer and healthier solutions to deal with my depression.
I came across a lot of different research and therapies.
I wasn’t sure if they would work, but then they did.
And I overcome my depression for good.
One of my most important discoveries was that nutrient deficiencies can make your depression worse.
And they could even be the root cause of it.
It made so much sense.
But why hadn’t anyone ever brought it up?
I delved deeper into the scientific literature, and I found MANY nutrient deficiencies that can contribute to depression.
I started increasing my intake of them.
And I got better.
Much better.
This new post includes 20 nutrient deficiencies that could be making you feel depressed.
Read on to learn more.
Vitamin Deficiencies That Can Cause Depression
1. Vitamin B12
“Lack of understanding of B12 is one of the greatest tragedies of modern medicine.”
Having sufficient levels of Vitamin B12 is necessary for optimal brain and mental health.
Unfortunately, a deficiency is very common, especially in older individuals and vegetarians and vegans.
And even if you eat meat and you’re young, you may still have a deficiency.
Poor gut health and even psychiatric medications can cause a deficiency.
In fact, it’s estimated that almost 40% of Americans are deficient today.
Numerous studies have shown that having a deficiency in Vitamin B12 leads to symptoms of depression (16-22).
And B12 levels tend to be significantly lower in people who are depressed (13).
In one study, subjects with Vitamin B12 deficiency were 2 times as likely to be severely depressed as non-deficient subjects (15).
Even a mild decrease in B12 levels is associated with mood disturbances (14).
Luckily, there are steps you can take if you’re deficient.
Vitamin B12 is found primarily in animal foods, and beef liver is an excellent source. I take beef liver capsules because I don’t like the taste of liver.
You may also want to supplement with Vitamin B12 because studies show that B12 supplementation significantly lowers homocysteine levels and reduces depressive symptoms (23-24).
If you decide to supplement, avoid the semisynthetic version of B12 (cyanocobalamin) and instead take the methylated form (methylcobalamin or methyl-B12).
Methyl-B12 is better absorbed and more biologically active.
2. Vitamin D (and Vitamin K2)
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that your skin synthesizes when exposed to the sun.
Every tissue in your body has Vitamin D receptors, including the brain, so a deficiency can lead to costly physiological and psychological consequences, including depression.
Researchers have found a very strong link between Vitamin D deficiency and depression (27-28).
The lower your Vitamin D levels, the more symptoms of depression you are likely to have (35).
Unfortunately, reports indicate that Vitamin D deficiency is widespread and a major health problem globally (25).
Researchers estimate that 50 percent of the general population is at risk of Vitamin D deficiency (26).
It’s best to get your Vitamin D by going outside and getting sunlight.
It’s especially important to make sure you get some sunlight in the morning to set your circadian rhythm.
But most people still don’t get enough Vitamin D from the sun, especially during the winter.
That’s why I recommend taking a Vitamin D supplement.
Research does show that taking a Vitamin D3 supplement is effective at reducing symptoms of depression and seasonal affective disorder (29-31).
This is likely because Vitamin D increases the production of numerous neurotransmitters, including serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine (32-34).
It's important to test and monitor your Vitamin D levels before and after supplementing with it.
Lastly, if you decide to supplement with Vitamin D3, you should consider taking it with Vitamin K2.
A recent study found that Vitamin K2 reduces depression in animals (36).
And Vitamin K2 is known to improve brain function in humans (37-38).
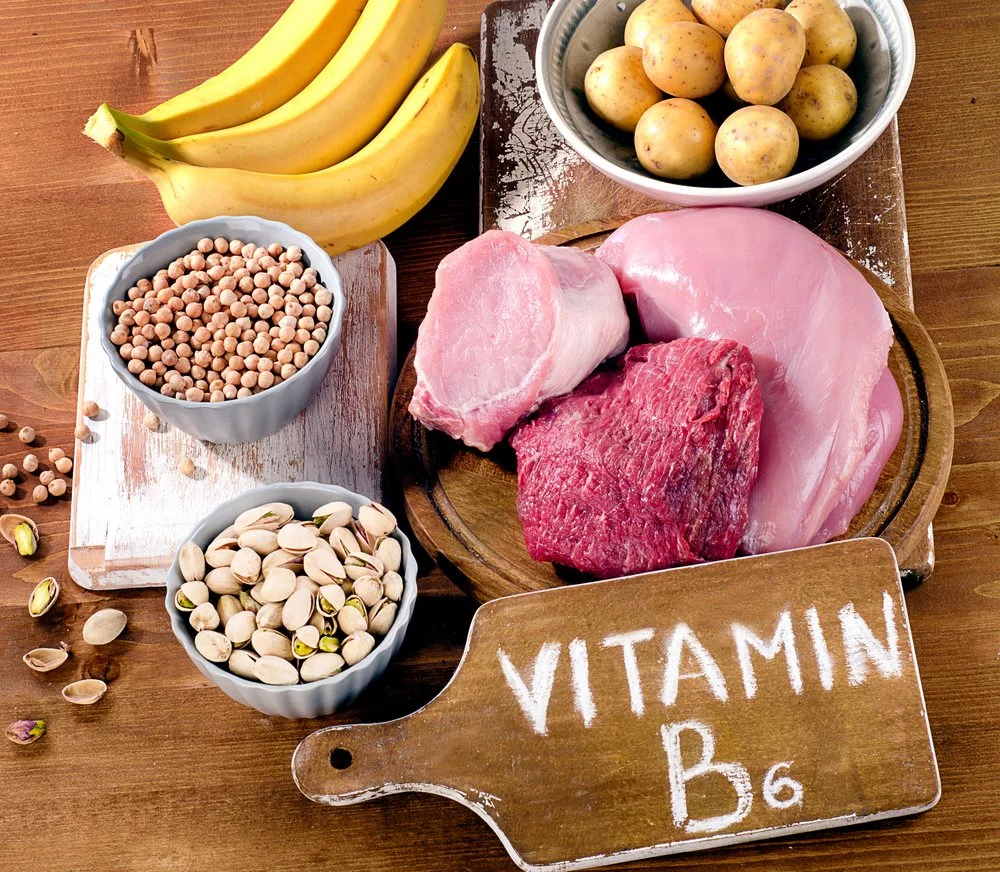
3. Vitamin B6
Having a deficiency in Vitamin B6 can also contribute to your depression.
It’s a key nutrient that supports your entire nervous system.
It can boost your mood because it plays a key role in the production of neurotransmitters in your brain, including serotonin and dopamine. It also lowers homocysteine.
Research shows that people with depressive symptoms tend to have low levels of Vitamin B6 (85-87).
A Vitamin B6 deficiency also contributes to chronic inflammation, which is one of the main underlying root causes of depression (88).
Fortunately, consuming more Vitamin B6 can help.
One study found that women that eat more foods containing Vitamin B6 have a lower risk of depression (89).
Some of the best food sources of Vitamin B6 include potatoes, bananas and chicken.
But supplementation is often necessary to see quick improvements.
One study found that supplementing with Vitamin B6 can reduce depressive symptoms by lowering homocysteine levels (90).
When I took antidepressants for depression, multiple functional and integrative doctors suggested I supplement with Vitamin B6.
This is because these medications can actually further deplete Vitamin B6, increasing depression in the long run.
Vitamin B6 is included in the Optimal Zinc supplement.
4. Vitamin C
Having low levels of Vitamin C can also make you feel depressed.
Researchers have found that poor Vitamin C status is associated with increased symptoms of depression (105).
Animal research also shows that a Vitamin C deficiency can lead to low levels of dopamine and serotonin in the brain, which causes mice to act depressed (106-107).
As you probably know, Vitamin C can be found in foods such as peppers, citrus fruits, green leafy vegetables, broccoli, tomatoes, and berries. These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Mental Health.
In addition to getting Vitamin C from fruits and vegetables, I take at least 500 grams of this Vitamin C every day.
I’ve experimented with taking up to 10 grams daily, and it definitely improved my mood and reduced my stress levels, especially when I was coming off antidepressants.
Research backs this up, showing that supplementing with Vitamin C can actually improve mood in both unhealthy and healthy individuals (95, 102-103).
Various other studies show that Vitamin C supplements reduce stress and anxiety and decrease the severity of depression (96-101, 104).
Studies even show that Vitamin C can increase the effectiveness of antidepressants (108-109).
5. Folate
Folate (Vitamin B9) is an essential B vitamin that plays a key role in methylation, one of the most important processes in your body and brain for optimal energy and nervous system function.
Researchers have found that if you are depressed, you likely have lower levels of folate circulating in your blood, and people with low blood folate are at greater risk for developing depression (55-56).
Good dietary sources of natural folate include:
Leafy greens
Asparagus
Broccoli
Cauliflower
Strawberries
Avocado
Beef liver
Poultry
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain and Mental Health.
However, eating folate-rich foods sometimes isn’t enough. In fact, many people do not get enough folate from food because cooking and food processing destroy natural folates (54).
And supplementation is often needed.
In one study, patients with depression took methylfolate for 6 months, and they witnessed a significant improvement in their depressive symptoms (57).
Researchers have even suggested that folate supplementation should be a first-line treatment for depression (58).
Methylfolate can be effective at treating depression because it helps lower homocysteine levels, helps produce serotonin and dopamine, and stimulates serotonin receptors in the brain (59-62).
6. Thiamine
Thiamine, also known as Vitamin B1, is an essential water-soluble nutrient that cannot be made by the body.
It’s used in nearly every cell in the body and especially important for supporting energy levels.
It’s also required by nerve cells and other supporting cells in the nervous system (167).
Research shows that lower levels of Vitamin B1 are associated with a higher prevalence of depressive symptoms (168).
Vitamin B1 deficiency is also known to lead to irritability and symptoms of depression (170).
Some doctors and researchers believe that postpartum depression is sometimes simply a Vitamin B1 deficiency (169).
Luckily, consuming more Vitamin B1 can help.
A randomized, double-blind clinical trial found that Vitamin B1 supplementation reduces symptoms of depression within 6 weeks (171).
And another concluded that Vitamin B1 supplementation improves mood, reduces brain fog, and speeds up reaction time (172).
In fact, researchers have even found that subjects’ mood improves if the amount of Vitamin B1 in their blood increases, and that the opposite occurs if the amount of Vitamin B1 in their blood decreases (173).
Healthy food sources of Vitamin B1 include green peas, beef liver, asparagus, pecans, spinach, sunflower seeds, macadamia nuts, oranges, cantaloupe and eggs.
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Mental Health.
7. Riboflavin
Riboflavin, also known as Vitamin B2, plays a key role in energy metabolism throughout your entire body.
As a result, a Vitamin B2 deficiency can affect the entire body, leading to low energy, weight gain, and depression.
In fact, lower levels of Vitamin B2 have been found in people with depression (91).
Researchers have also found that Vitamin B2 consumption decreases risk of postpartum depression (92).
Healthy food sources of Vitamin B2 include pastured eggs, leafy vegetables, beef liver, mushrooms, sunflower seeds, and almonds.
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Mental Health.
If you’d like, you can also supplement with Vitamin B2.
Studies show that supplementing with Vitamin B2 helps lower homocysteine and reduces depressive symptoms (93-94).
Vitamin B2 is included in the Optimal Zinc supplement.
8. Inositol
Inositol is a naturally-occurring molecule found in nearly all plants and animals. It plays a key role in various biological processes.
The brain has the highest concentration of inositol, where it plays an important role making neurotransmitters (124).
Inositol can be found in many foods, particularly fruit, especially cantaloupe and oranges (125).
It used to be considered a B Vitamin, called Vitamin B8. But it currently is no longer considered an essential nutrient because your body can produce inositol from glucose (126).
But I’m including it in this list anyway because individuals with depression have very low levels of inositol in their brains (127-129).
And inositol supplementation has been shown to increase inositol levels and help treat depression (130, 132).
It can also reduce symptoms of depression in women with premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (131, 133).
It’s even been shown to help patients who have discontinued their antidepressant medication (134).
I took high doses of inositol powder when weening off psychiatric medication.
Check out my full post about inositol to learn more about the benefits.
Fun fact: Inositol is also used as a stand-in for cocaine in television shows and movies.
9. Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a coenzyme and antioxidant located primarily in the mitochondria. It has numerous known health benefits and plays a critical role in producing energy for the body.
CoQ10 is produced within the body, but it’s also found within food and can be supplied to the body through food or supplementation. It resembles a fat-soluble vitamin.
Meat and fish are the richest sources of dietary CoQ10, including beef, pork, chicken heart, and chicken liver. Nuts and some oils also contain some CoQ10 (110).
Research shows that CoQ10 levels are reduced in people with depression and chronic fatigue (111).
One study also found that CoQ10 regulates serotonin levels and depressive symptoms in fibromyalgia patients (117).
CoQ10 supplementation has also been shown to improve fatigue and reduce depression symptom severity (112-114).
It also displays antidepressant-like activity in animals (115-116).
Mineral Deficiencies That Can Cause Depression
10. Magnesium
Magnesium is a vital mineral that participates in more than 300 biochemical reactions in your body.
Unfortunately, a lot of people are deficient in magnesium today.
This is a shame because magnesium is absolutely essential for the proper functioning of your nervous system and optimal neurotransmitter activity.
Research shows that low magnesium levels contribute and worsen many neuropsychiatric problems, including depression (42).
In fact, researchers have found that people with depression have lower magnesium levels than healthy people (49).
They’ve also found a significant association between very low magnesium intake and depression (43).
On top of this, animal research shows that removing magnesium from their diet results in depressive-like symptoms (50).
So if you’re struggling with depression, it’s very important to make sure you’re getting enough magnesium so that you don’t have a deficiency.
Luckily, there are a number of ways to do this.
First, make sure you’re eating magnesium-rich foods on a regular basis, including:
Spinach
Chard
Pumpkin seeds
Almonds
Avocado
Dark chocolate
Bananas
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Mental Health.
Epsom salt baths are another great way to increase your body’s intake of magnesium.
I also highly recommend a high-quality supplement that includes magnesium.
Magnesium is included in this supplement.
A number of studies have concluded that magnesium supplementation can reduce depressive symptoms in humans – sometimes within 7 days (44-48).
Since most people are deficient, magnesium is one of the three supplements that I think everyone should be taking.
11. Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral for mental health.
Like magnesium, it plays a key role in neurotransmission and nervous system functioning.
Mounting evidence suggests a link between zinc deficiency and the development and severity of depression (66-68, 76).
Depressed patients tend to have lower levels of zinc. And as their zinc levels drop, their depressive symptoms get worse (81-84).
Unfortunately, it’s estimated that 2 billion people in the world are deficient in zinc, and several studies show that even subclinical deficiency of zinc impairs brain function in children and adults (63-65).
So, if you struggle with depression, it’s quite possible that you’re deficient, and you’ll definitely want to optimize your zinc levels.
Some of the best food sources of zinc include:
Oysters
Grass-fed beef
Pumpkin seeds
Cashews
Mushrooms
Spinach
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain and Mental Health.
However, if you’re deficient like I was, I recommend taking a high-quality zinc supplement, at least for a short period of time.
A meta-analysis and several studies have concluded that zinc supplementation has antidepressant effects and significantly reduces symptoms of depression. One way it improves mood is by significantly increasing BDNF levels (69-75, 77-80).
I created and take the Optimal Zinc supplement to make sure my zinc levels are optimal.
Check out my previous post all about zinc if you’re interested in discovering more steps you can take to increase your zinc levels.
12. Iron
Iron is a trace mineral found in every living cell in our bodies.
It carries oxygen to all parts of your body, and low levels can leave you feeling tired, pale, irritable and foggy.
Sounds like depression doesn’t it?
Several studies show that iron deficiency increases the risk of developing depression and increases the severity of depression (184-186, 188-190).
Researchers have also conducted a meta-analysis and found that high iron intake reduces the chance of developing depression (183).
In one study, iron supplementation resulted in a 25% improvement in depressive symptoms (187).
Despite this, I don’t actually recommend supplementing with iron though because some research suggests that too much iron can cause health problems.
It’s definitely preferable to get your iron from food.
I make sure I get enough iron simply by taking grass-fed beef liver capsules.
Beef liver is one of the best sources of iron, but I don’t like the taste, so I go with the capsules.
Other good sources of iron include:
Spirulina
Dark chocolate
Spinach
Sardines
Pistachios
Raisons
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Mental Health.
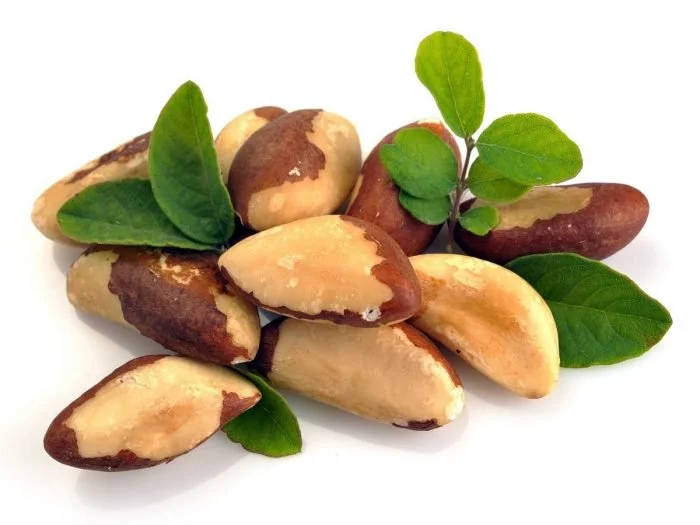
13. Selenium
Selenium is an essential trace mineral that is important for many bodily processes that affect your brain and mental health.
Researchers have found that depression is associated with low levels of selenium (191).
But supplementing with selenium has been shown to significantly increase selenium levels and improve symptoms of depression (192).
Other research shows that selenium intake is associated with a general elevation of mood (193).
Brazil nuts are the richest dietary source of selenium, but it can also be found in wild-caught seafood, pastured chicken and eggs, and grass-fed meat.
I also make sure I’m not deficiency in selenium by supplementing with it.
Selenium is included in this supplement.
14. Manganese
Manganese is an important trace mineral for human health. It acts as a cofactor, helping many enzymes carry out their functions in the body.
Research shows that having low levels of manganese can contribute to the development of depression (135).
One study found that depressed patients had significantly lower levels of “manganese superoxide dismutase”, which is a manganese-dependent enzyme (136).
Researchers have also found that women with higher manganese intake had a lower prevalence of depressive symptoms (137).
Hazelnuts and macadamia nuts contain high levels of manganese, while leafy green vegetables, tea, chocolate and some fruits contain moderate levels (139).
However, it’s important to note that you shouldn’t consume too much manganese.
In excess, manganese is neurotoxic and can lead to manganism, a neurodegenerative disorder that causes dopaminergic neuronal death and symptoms similar to Parkinson's disease (138).
So I definitely don’t recommend supplementing with large doses of manganese.
The small amount of manganese in Optimal Antiox is fine though. It’s what I take.
Fatty Acid Deficiencies That Can Cause Depression
15. Dihomo-Gamma-Linolenic Acid
Dihomo-Gamma-Linolenic Acid (DGLA) is an uncommon fatty acid.
It’s made in the body by the elongation of Gamma Linolenic Acid (GLA).
But small amounts can also be found in animal products (118).
Last year, researchers found that people with depression are more likely to have low levels of DGLA levels (121).
And increasing DGLA levels may lower the risk of developing depression (122).
DGLA also has anti-inflammatory effects in the body (119).
So it makes sense that levels would be low in depressed individuals because an increasing amount of evidence suggests that depression is a chronic inflammatory disease.
DGLA can be increased by supplementing with dietary GLA (120).
GLA can be found in Borage Oil, Evening Primrose Oil and Blackcurrant Seed Oil (123).
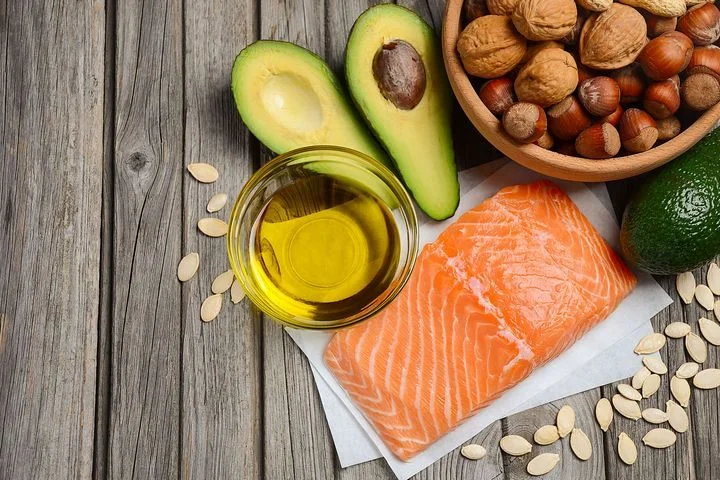
16. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s fatty acids are the highest quality fats for the brain and increasing your intake of them is one of the most impactful actions you can take to fight depression.
Several studies have shown that depressive patients have lower levels of omega-3 fatty acids (1-3).
Researchers even conducted a meta-analysis of 14 studies, and they found that levels of omega-3 fatty acids were significantly lower in people with depression (4).
They concluded that having a deficiency in omega-3 fatty acids is a “contributing factor to mood disorders” (5).
It’s important to consume enough omega-3 fatty acids because they are essential fats that your body cannot produce itself.
Omega-3 fatty acids are found primarily in cold water fish, including:
Salmon
Black cod
Sablefish
Sardines
Herring
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Mental Health.
Unfortunately, most people don't consume enough omega-3 fatty acids through their diet.
That’s why I recommend supplementing with krill oil, a special kind of fish oil that contains the essential omega-3 fatty acids.
Plenty of research shows that omega-3 supplements are effective at treating clinical depression – just as effective as antidepressants drugs – because they lower inflammation in the brain (6-10).
Amino Acid Deficiencies That Can Cause Depression
17. Carnitine
Carnitine is an amino acid found in nearly every cell of the body. It plays a vital role in the production of energy.
Researchers have found significantly lower levels of carnitine in patients with depression. And their low carnitine levels are associated with the severity of their depression (11-12, 174-175).
Carnitine is mainly found in meat, fish and poultry.
But you can also supplement with it.
I recommend Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR), an acetylated form of carnitine. It’s best supplemental form of carnitine.
It’s often used as a natural brain booster because it increases alertness and provides support to brain cells.
But it’s also been shown to be very effective at quickly improving mood and treating depression (179-182).
Six randomized clinical trials have demonstrated that ALCAR is better at treating depression than placebo (177).
And two other studies found that ALCAR improved depressive symptoms in patients with chronic depression, and it was just as effective as antidepressant medications, but with less side effects (176, 178).
ALCAR is included in the Optimal Brain supplement.
Make sure you read this article to learn more about the remarkable benefits of ALCAR.
18. Glutamine
Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the body, suggesting that it’s very important.
It’s also one of the few amino acids that can directly cross the blood-brain barrier.
Glutamine is a conditionally essential amino acid, meaning the body can usually produce sufficient amounts of it. But sometimes the body uses up so much glutamine that it becomes necessary to obtain it from the diet or supplements, particularly during periods of illness, stress, inflammation and injuries (156-157).
Researchers have found that depressed adults have reduced levels of glutamine (158).
And glutamine deficiency has been shown to increase depressive-like behaviour in animals (159).
But glutamine supplementation has “clear anti-depressive properties” and has been shown to improve mood (160-161).
High levels of glutamine can be found in protein-rich foods such as beef, chicken, fish and eggs. Beets, cabbage, spinach, carrots, parsley, brussel sprouts, celery, kale and fermented foods like miso also contain some glutamine.
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Mental Health.
Glutamine is also available in supplement form.
Glutamine was one of the main supplements that helped me heal my leaky gut, but I no longer need to take it regularly.
19. Tryptophan
Tryptophan is an essential amino acid that cannot be produced by the body. It must be consumed through diet or by taking supplements.
Some healthy foods that contain tryptophan include bananas, chicken, turkey and dark chocolate (140).
Tryptophan helps produce the neurotransmitter serotonin. It’s converted to 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) in the brain, which then produces serotonin (141-142).
Researchers have found that depressed patients have significantly lower levels of tryptophan in their blood than healthy control subjects (143-144).
Studies also show that depressed patients have a decreased ratio of tryptophan to neutral amino acids in their blood. This suggests that tryptophan availability to the brain is likely reduced in depressed patients (145-146).
Personally, supplementing with tryptophan never helped me. In fact, it always seemed to make me worse. It gave me asthma and acne and increased my depression.
This is because depressed patients sometimes have problems creating serotonin from tryptophan. Instead, they create other metabolites from tryptophan, such as quinolinic acid, which can be toxic. For depressed patients like me, tryptophan supplementation won’t help, and may actually make their depression worse (150-151).
However, some people do see their mood improve when they increase their intake of tryptophan. So it shouldn’t be completely disregarded.
There are studies that show that consuming a high tryptophan diet and consuming additional dietary tryptophan can increase mood and lead to significantly less depressive symptoms (152-154).
So supplementing with tryptophan is worth a shot if you’re struggling with depression and haven’t tried it yet. Just be aware of possible side effects.
If you want, you can also try supplementing with 5-HTP instead of tryptophan. 5-HTP is the direct precursor to serotonin.
5-HTP is included in this supplement.
20. Glutathione
Glutathione is a small peptide made up of 3 important amino acids – glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine – each of which have several important roles in the human body.
Glutathione is found in the food supply and within the human body, where it acts as an antioxidant. It is used by every cell in the body.
It’s technically not an “essential nutrient” because the body can create it.
However, it’s still very important, and a glutathione deficiency leads to increased susceptibility to oxidative stress, which is thought to be involved in a number of diseases, including depression.
Studies show that patients with depression have significantly lower levels of glutathione. And the lower a person’s glutathione levels, the more depressed they are likely to be (162-164).
Some practitioners and researchers have found that increasing glutathione intake and levels can successfully treat depression (165).
Glutathione is also able to prevent behavioural depression in animals (166).
It’s important to note that standard glutathione supplements are not very effective at increasing glutathione levels because they are not well absorbed by the body.
N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) is a tried-and-true way of increasing glutathione levels because it’s the direct precursor to glutathione.
Garlic, asparagus, and cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli and kale, can also help boost glutathione levels, but NAC supplements are more powerful.
Other supplements that have been shown to help increase and maintain optimal glutathione levels include Selenium, Alpha Lipoic Acid, and S-adenosyl-methionine (Sam-E).
Enjoy This Article? You Might Also Like My FREE Food Guide for Optimal Brain and Mental Health!
References:
(1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20452573
(2) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16741195
(3) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4369545/
(4) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20452573
(5) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16741195
(6) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24805797
(7) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20586692
(8) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20439549
(9) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3976923/
(10) https://examine.com/supplements/fish-oil/
(11) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24611884
(12) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5470074/
(13) https://examine.com/suhttps://examine.com/supplements/vitamin-b12/plements/vitamin-b12/
(14) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2781043/
(15) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10784463
(16) https://examine.com/supplements/vitamin-b12/
(17) https://wellnessmama.com/36091/vitamin-b12-deficiency/
(18) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22276208
(19) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2781043/
(20) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10784463
(21) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3262813/
(22) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24339839
(23) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24339839
(24) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21771745
(25) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19543765
(27) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27750060
(28) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23377209
(29) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10888476
(30) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22191178
(31) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4011048/
(32) https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/02/150225094109.htm
(33) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9011759
(34) https://examine.com/supplements/vitamin-d/
(35) https://examine.com/supplements/vitamin-d/
(36) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28068285
(38) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24108469
(39) http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00048670802534408
(40) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10746516
(41) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9861593
(42) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27807012
(43) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25748766
(44) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2067759
(45) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19271419
(46) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1672392
(47) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23950577
(48) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16542786
(49) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19780403
(50) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18825946
(51) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/5314166
(52) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14769778
(53) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17522618
(54) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12493090
(55) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10967371?dopt=Abstract
(56) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15671130
(57) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1974941
(58) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1810582/
(59) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21771745
(60) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18950248
(61) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19796883
(62) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23212058
(63) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22664333
(64) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21939673
(65) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22673824
(66) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3868572/
(67) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20689416
(68) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18655800
(69) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15145706
(70) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18766297
(71) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24621065
(72) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/
(73) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21798601
(74) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24130605
(75) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16491668
(76) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20689416
(77) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21798601
(78) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18191237
(79) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3022308/
(80) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24621065
(81) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20013161
(82) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20493532
(83) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9276075
(84) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8071476
(85) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15479988
(86) http://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/vitamin-B6
(87) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15479988
(88) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23550784
(89) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26648330
(90) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21771745
(91) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22081620
(92) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16815556
(93) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21771745
(94) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1578091
(95) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20688474
(96) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26353411
(97) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24511708
(98) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3599706/
(99) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12208645
(100) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4376513/
(101) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4376513/
(102) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3599706/
(103) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12208645
(104) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4376513/
(105) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25835231
(106) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23106783
(107) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3325330/
(108) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4376513/
(109) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3599706/
(110) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20301015h.gov/pubmed/20301015
(111) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20010493
(112) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22467846
(113) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4414830/
(114) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25603363
(115) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23313551
(116) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23928691
(117) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24525646
(118) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dihomo-%CE%B3-linolenic_acid
(119) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dihomo-%CE%B3-linolenic_acid
(120) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dihomo-%CE%B3-linolenic_acid
(121) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28235735
(122) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28235735
(123) https://academic.oup.com/jn/article/128/9/1411/4722487
(124) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inositol
(125) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7416064
(126) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inositol
(127) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mrm.21709/full
(128) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15953489
(129) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9247405
(130) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24424706
(131) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hup.1241/abstract
(132) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0062698/
(133) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22031267
(134) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7726322
(135) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25712638
(136) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25171019
(137) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28110159
(138) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manganese#Biological_role
(139) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4516557/
(140) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2908021/
(141) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21071157
(142) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28118532
(143) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2521647
(144) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/016517819390102M
(145) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2521647
(146) https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/article-abstract/492559
(147) https://goo.gl/5rBaMM
(148) https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/article-abstract/492559
(149) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29109914
(150) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26654774
(151) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4955923/
(152) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4393508/
(153) https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/j.1600-0447.2011.01706.x
(154) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11869656
(155) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8775762
(156) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3425386/
(157) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2668703
(158) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17283286
(159) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3633711/
(160) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8289407
(161) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1020692
(162) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3964749/
(163) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21552194
(164) https://academic.oup.com/ijnp/article/14/1/123/657694
(165) https://goo.gl/hcyoey
(166) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7972287
(167) http://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/arh27-2/134-142.htm
(168) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3521461/
(169) https://goo.gl/CKdRbW
(170) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26984349
(171) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26984349
(172) https://goo.gl/7xi241
(173) https://goo.gl/7xi241
(174) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28670223
(175) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23574341
(176) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16316746
(177) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24607292
(178) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24607292
(179) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18491985
(180) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23382250
(181) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28670223
(182) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15591014
(183) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28189077
(184) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3680022/
(185) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29603506
(186) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17063146
(187) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15671224/
(188) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29363366
(189) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29307706
(190) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22286844
(191) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18463429
(192) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18463429
(193) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1873372
(194) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16184071