Acetylcholine is one of the most important neurotransmitters.
It's critical for the optimal functioning of your brain.
And you’ll definitely want to optimize your levels, especially if you’re looking to improve your memory, attention, sleep and learning abilities.
Luckily, there are a number of ways you can increase the acetylcholine levels in your brain.
And this article shares the best strategies with you.
This post includes six main sections:
The benefits of increasing acetylcholine and how it affects brain function
The conditions associated with low levels of acetylcholine
The best choline supplements you can take to increase acetylcholine production
The best foods and nutrients you should eat to raise acetylcholine
The best herbal supplements for boosting acetylcholine
And the most important hormones for optimal acetylcholine levels
Continue reading to learn more and discover how you can naturally improve your acetylcholine levels.
The Benefits of Increasing Acetylcholine and How It Affects Your Brain
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter, meaning it’s a chemical messenger released by neurons (nerve cells) to “communicate” with other neurons.
In 1914, it was the very first neurotransmitter to be identified within the brain (82-83).
Researchers have found that acetylcholine acts on the entire nervous system and plays a large variety of roles throughout the brain.
But it’s most commonly associated with improved memory and learning (84-85).
The brain actually needs enough acetylcholine to form memories.
Research shows that acetylcholine plays a central role in synaptic plasticity, which is a process in the brain that allows brain cells to store new information and memories (88).
Scopolamine is a drug that blocks acetylcholine activity, and it’s known to impair learning and memory in both humans and animals (86-87).
What’s also interesting is that acetylcholine levels have even been shown to rise during REM sleep, which is the stage of sleep when humans “store and consolidate” new memories (89-91).
But acetylcholine doesn’t just improve your memory and learning abilities.
New studies suggest it helps you stay awake, alert and focused (92-93).
In fact, some stimulant drugs such as amphetamines and cocaine increase the activity of acetylcholine in the brain, and researchers think acetylcholine may be responsible for the wakefulness-promoting effects of these drugs (94).
Lastly – but perhaps most importantly – acetylcholine can promote relaxation by stimulating the vagus nerve.
Research shows that acetylcholine can stimulate vagus nerve activity, which can reduce brain inflammation and improve cognitive function and mental health (95, 99).
Surprisingly, acetylcholine is the main neurotransmitter of the “rest-and-digest” parasympathetic nervous system. It activates the parasympathetic nervous system and counteracts “fight-or-flight” tendencies (96-98).
Conditions Associated with Low Levels of Acetylcholine
As we get older, acetylcholine activity slowly becomes less and less efficient. Less acetylcholine is released from brain cells, and cells become less sensitive to the acetylcholine that’s released.
Studies suggest that this is one reason why memory starts to fail in older people (100).
But besides aging, low acetylcholine levels (and reduced acetylcholine activity in certain areas of the brain) have also been linked to the development and progression of several brain and mental health conditions.
The biggest link is with Alzheimer's disease and dementia, as people with these conditions often have low acetylcholine levels (101-102).
In fact, it’s estimated that patients with Alzheimer’s Disease lose 90% of the acetylcholine in their brains (107).
Research shows that low acetylcholine in the brain can cause cognitive decline and poor memory in people with dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
And many of the medications that are prescribed to relieve cognitive symptoms and slow down the disease’s progression often work by increasing acetylcholine in the brain and stimulating acetylcholine activity throughout the brain (103-112).
Parkinson’s disease is another neurodegenerative disorder that is linked to low acetylcholine levels in the brain (113).
Too little acetylcholine in the brain can also contribute to the poor cognition and psychosis seen in people suffering with schizophrenia (114-115).
It’s also been found that patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis have lower acetylcholine levels (116).
Lastly, children with autism may lack acetylcholine in their brain, which can contribute to their intellectual impairment. But increasing acetylcholine can improve cognitive and social symptoms (117-118).
It’s also important to point out that many prescription medications are anticholinergic, meaning they reduce acetylcholine and inhibit the physiological action of acetylcholine in the brain.
I used to be on several prescription drugs that were anticholinergic, and I experienced a gradual decline in my cognition.
But once I started following and implementing some of the steps below, I noticed an improvement in cognitive function since they increased my levels of acetylcholine.
I still follow much of the advice below because it helps me focus, remember and learn more effectively.
The Best Choline Supplements to Increase Acetylcholine in the Brain
One of the best and most straightforward approaches to increasing acetylcholine levels is by supplementing with choline.
Choline is an essential nutrient, meaning it can’t be made by the body. You must consume it through your diet.
Unfortunately, most people don’t eat enough choline because very few foods in the Western diet contain high amounts of it.
This is a huge problem because choline is a precursor to acetylcholine. It’s one of the important building blocks that the brain needs to make acetylcholine. You need to eat enough choline to synthesize enough acetylcholine in your brain.
And in one study, researchers found that a higher intake of choline was associated with better cognitive performance (79).
There are several types of choline supplements on the market, and many of them claim to increase choline and boost acetylcholine levels in the brain.
But unfortunately, many of them are not effective at increasing choline levels in the brain and raising acetylcholine.
I’ve tried all of the main choline supplements over the years.
And I’ve found the two below to be the most effective and best options.
That’s why they're now both included in the Optimal Brain supplement.
1. Citicoline
Citicoline (also known as CDP-Choline) is one of the most bioavailable supplemental forms of choline.
It has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.
Research shows that citicoline increases choline levels in the brain (1).
Since choline helps produce acetylcholine, citicoline also increases acetylcholine in the brain (2, 5-6).
Researchers have found that citicoline increases the synthesis and release of acetylcholine in the brain after traumatic brain injury. It also increases the number of acetylcholine receptors in your brain (4,7).
As a result, supplementing with citicoline can improve cognition, working memory and verbal memory, and attention (80-81).
Citicoline significantly improves my focus and mental energy. That’s why it’s in the Optimal Brain supplement.
Make sure you read this article to learn more about the remarkable benefits of Citicoline.
2. Alpha GPC
Alpha GPC is another excellent supplemental form of choline. It’s very effective at reaching the brain and improving cognitive function.
Researchers have found that Alpha GPC enhances cognition and improves learning and memory by increasing the release of acetylcholine in the brain (8).
One study found that it increases levels of acetylcholine in the frontal cortex region of the brain, which improves memory, judgment and decision making (10).
Alpha GPC can also increase the synthesis of acetylcholine in the brain, which can help treat dementia (9).
Alpha GPC is in Optimal Brain along with citicoline.
Make sure you read this article to learn more about the remarkable benefits of Alpha GPC, the optimal dosage, and the best way to take it.
The Best Foods and Nutrients to Increase Acetylcholine in the Brain
3. Pantethine
Pantethine is the bioactive form of Vitamin B5.
It’s the precursor to coenzyme A. And coezyme A plays a key role in the synthesis of acetylcholine.
So supplementing with pantethine can lead to an increase in the synthesis of acetylcholine in the brain (11-13).
Researchers have found that chronic alcohol consumption is known to deplete pantethine in the brain. This then inhibits coenzyme A and reduces levels of acetylcholine in all areas of the brain (11-13).
So it’s best to avoid alcohol if you want to increase your acetylcholine levels.
And if you do drink alcohol regularly, definitely supplement with pantethine so that you can maintain your acetylcholine levels.
Pantethine is one of my favourite supplements for energy, focus and motivation.
That’s why I included it in the Optimal Energy supplement.
Pantethine is also a key part of Dr. Bredesen’s protocol for preventing dementia.
4. Acetyl-L-Carnitine
Acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR) is an acetylated form of the amino acid carnitine.
It’s been shown to have neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing effects.
It’s often used as a natural brain booster by people of all ages because it supports brain cells, enhances cognition, and increases alertness.
One reason it works so well is because it’s the precursor to acetylcholine and increases levels of acetylcholine in the brain. It also activates acetylcholine receptors in the brain (14-15).
As a result, researchers believe it should be used to treat cognitive decline (16).
I find that ALCAR personally gives me a big boost in cognitive energy and resilience. It keeps me motivated to do complex tasks that require optimal brain function.
It’s included it in the Optimal Brain supplement.
Make sure you read this article to learn more about the remarkable benefits of ALCAR.
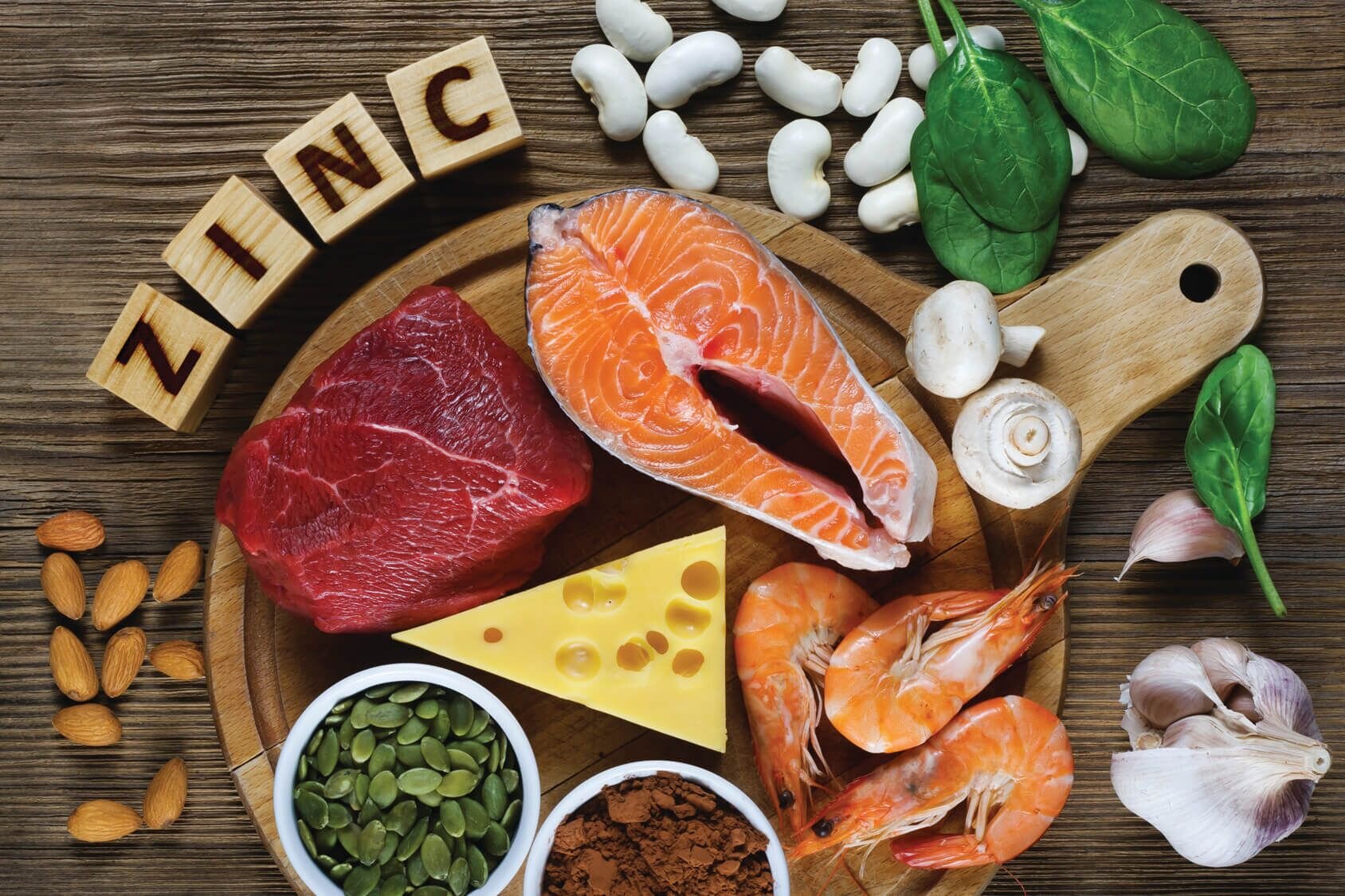
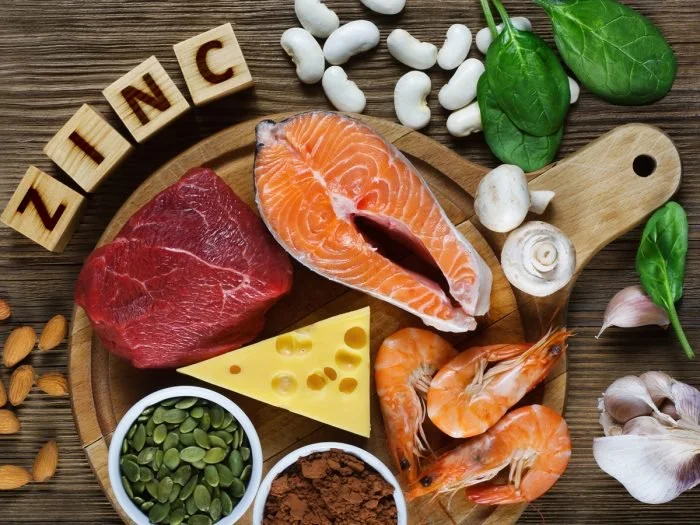
5. Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral for brain health.
Unfortunately, it’s estimated that 2 billion people in the world are deficient in zinc, and several studies show that even subclinical zinc deficiency impairs brain function (75-77).
That’s a huge problem.
Because studies show that zinc significantly inhibits acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme that breaks down and reduces acetylcholine. As a result, it increases acetylcholine levels (23).
Researchers have also found that zinc activates acetylcholine receptors in the brain (24-25).
I created and take the Optimal Zinc supplement to make sure my zinc levels are optimal. I created it because I want to give my clients and readers the very best zinc supplement so that they can experience superior results. I have found that many zinc supplements on the market fall short. Optimal Zinc includes several other nutrients (co-factors) that increase the absorption of zinc.
Besides supplementing with zinc, you should also eat plenty of healthy, whole foods that contain zinc.
Some of the best foods to optimize your zinc levels include:
Oysters
Grass-fed beef
Pumpkin seeds
Cashews
Mushrooms
Spinach
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain Health.
Check out my previous post all about zinc for more steps you can take to increase your zinc levels.
6. Epigallocatechin Gallate
Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) is the main polyphenol found in green tea.
It’s been shown to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.
Research shows that EGCG improves cognitive function by increasing cholinergic neurotransmission in the brain (26).
I personally drink organic green tea regularly, usually in place of coffee on days when I’m relaxing.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that the body isn't very good at absorbing EGCG from green tea and distributing it to the brain and other tissues.
That's why researchers often use large dosages of concentrated EGCG in their studies instead of green tea.
But unfortunately, large dosages of concentrated EGCG have been shown to cause liver toxicity.
So you could supplement with large dosages of concentrated EGCG and see some benefits.
But you'd be damaging your liver at the same time.
Not good.
So what should you do? How do you absorb EGCG and get the amazing benefits of it without damaging your liver?
You take it with Vitamin C.
Research shows that you can enhance the absorption and availability of EGCG by taking it with Vitamin C.
That's why the Optimal Antiox supplement includes a small and safe amount of EGCG, plus 500 mg of Vitamin C.
This significantly enhances the absorption of EGCG, and ensures you get all the brain and mental health benefits of EGCG (without the harm).
7. Grape Seed Extract
Grape seed extract is a supplement high in antioxidants that can help prevent memory loss and improve cognitive function.
Grape seed extract contains high levels of an antioxidant called proanthocyanidin.
Proanthocyanidin has been shown to increase acetylcholine levels and decrease the breakdown of acetylcholine in the brain (27).
And one study found that taking grape seed extract every day can improve attention and memory (78).
Grape seed extract is included in Optimal Antiox, and it contains 95% proanthocyanidins so that you get optimal results.
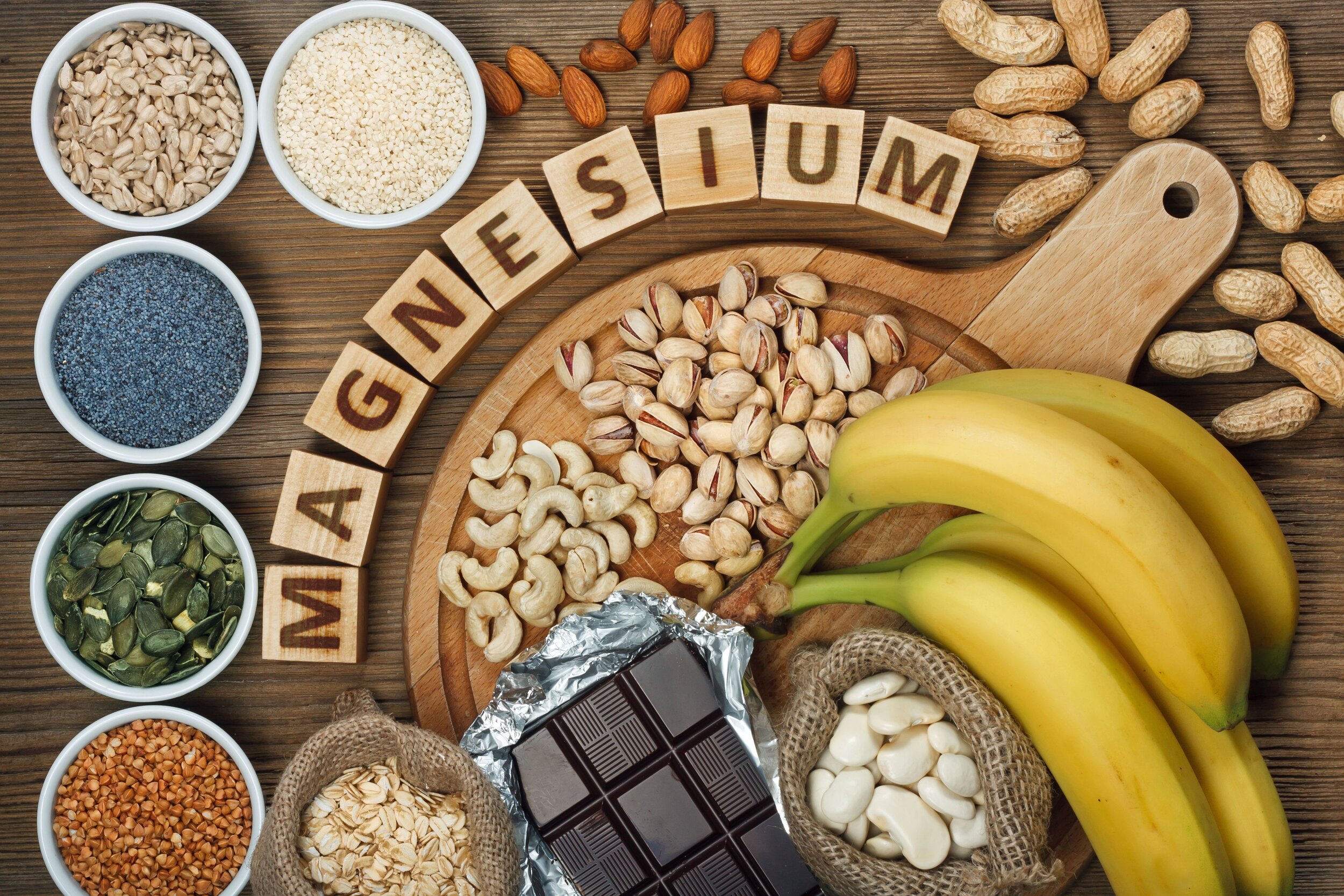
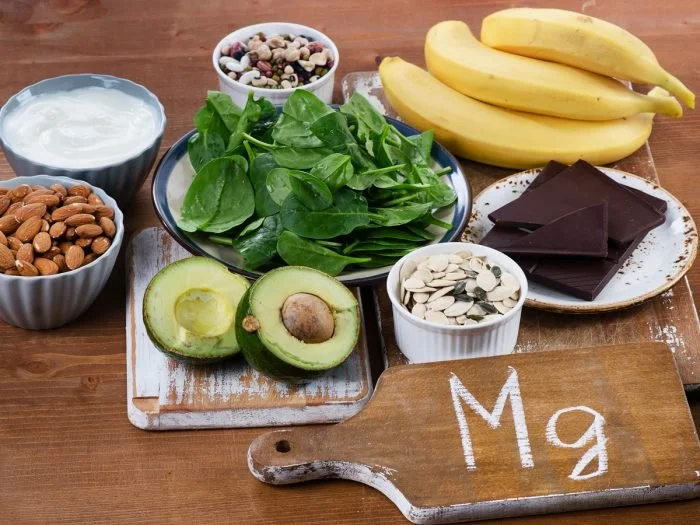
8. Magnesium
Magnesium is a vital mineral that participates in more than 300 biochemical reactions in your body.
Unfortunately, a lot of people are deficient in magnesium.
This is a shame because magnesium is absolutely essential for optimal brain function.
Magnesium has been shown to have a strong accelerating action on the synthesis of acetylcholine (28).
The mineral also increases the effectiveness of drugs that slow down the breakdown of acetylcholine (29).
Since most people are deficient, magnesium is one of the three supplements that I think everyone should be taking every day.
Epsom salt baths are another great way to increase your body’s intake of magnesium.
You should also make sure you’re eating enough magnesium-rich foods on a regular basis, including:
Spinach
Chard
Pumpkin seeds
Almonds
Avocado
Dark chocolate
Bananas
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain Health.
9. Manganese
Manganese is an important trace mineral for human health. It acts as a cofactor, helping many enzymes carry out their functions in the body.
Manganese has been shown to increase the synthesis of acetylcholine (30).
Hazelnuts and macadamia nuts contain high levels of manganese, while leafy green vegetables, tea, chocolate and some fruits contain moderate levels. These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain Health.
However, it’s important to note that you shouldn’t consume too much manganese.
In excess, manganese is neurotoxic and can lead to manganism, a neurodegenerative disorder that causes dopaminergic neuronal death and symptoms similar to Parkinson's disease.
So I don’t recommend supplementing with very large doses of manganese.
The small amount of manganese in Optimal Antiox is fine though.
10. Curcumin
Curcumin is the most heavily researched compound within turmeric, the spice that gives curry its yellow colour.
It’s one of my favourite natural compounds for the brain.
One reason is becayse the curcuminoids in turmeric significantly inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, increasing levels in the brain. As a result, turmeric can improve memory and help treat Alzheimer's disease (31).
Curcumin has also been shown to enhance the activity of acetylcholine in the brain (32-33).
Curcumin is included in the Optimal Energy supplement.
Since curcumin is a fat soluble, take it with a fatty meal.
11. Coffee
Coffee and caffeine are excellent for brain health.
There is lots of research showing they are very healthy and can lower the risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases.
One reason is because they can help optimize acetylcholine levels.
Research shows that caffeine enhances the release of acetylcholine and increases acetylcholine levels in the brain, particularly in the hippocampus, which is the “memory center” of the brain (17-18).
I recently cut out coffee completely but I used to drink this high-quality coffee.
You can also just take pure caffeine tablets if you want.
Coffee and caffeine can disrupt sleep though, so make sure you don’t drink it in the evening close to bed.
Some people like me are really sensitive and have to stop drinking it very early in the day so that it doesn’t disrupt their sleep. I would have my last cup sometime between 10 in the morning and noon. Any later than that and it disrupted my sleep.
It's also a good idea to try to consume the whole coffee fruit, instead of just coffee or pure caffeine.
Traditionally, the coffee bean is extracted from the coffee fruit for roasting. And the surrounding fruit is discarded.
But that’s a problem because the coffee fruit contains several healthy compounds not found in coffee beans themselves.
And researchers have found that consuming whole coffee fruit concentrate can significantly enhance cognitive functioning.
That’s why I included coffee fruit in the Optimal Brain supplement.
12. Eggs
Eggs are one of the richest food sources of choline.
And research shows that eating eggs can lead to a significant increase in choline levels in the blood and in the brain (19-20).
I eat at least 3 eggs every day. They are full of nutrients and excellent for brain health. You should try to find pastured eggs from a local farmer in your area.
Eggs are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain Health.
13. Beef Liver
Beef liver is another very rich source of choline.
And research shows that eating liver can lead to a significant increase in choline levels in the blood and in the brain (19-20).
Beef liver is one of my three top foods I recommend eating for optimal brain health.
It’s included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain Health.
I don’t like the taste of cooked liver, so I take desiccated beef liver capsules instead.
14. Uridine
Uridine is a natural compound commonly found in beer.
I definitely don’t recommend drinking beer, but supplementing with pure uridine can protect the brain, enhance cognition, and increase mood and motivation.
Researchers have found that supplementing with uridine increases acetylcholine concentrations in the brain (3).
It’s important to note that uridine in food is not bioavailable, and no food has been shown to increase blood levels of uridine (74).
So you’ll need to supplement with it.
Uridine is synergistic with omega-3 fatty acids and choline, meaning they all work better when you take them together.
15. Wild Blueberries
If you want to improve your cognitive performance, eating lots of fruits and vegetables is definitely something you’ll want to do regularly.
Wild blueberries are particularly potent because of they are so rich in polyphenols.
The polyphenols in wild blueberries have been shown to significantly improve learning and memory by increasing acetylcholine levels in the brain (21-22).
If you eat blueberries, make sure they are wild because they are richer in polyphenols.
I buy wild blueberries every time I go grocery shopping.
They are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain Health.
I try to eat one cup of them every day to support my brain health.
Alternatively, you can take a blueberry extract.
In fact, most researchers use a concentrated blueberry extract instead of actual blueberries when they study the beneficial health effects of blueberries.
It’s actually less expensive in the long run to take an extract than eat blueberries every day, but I just prefer to eat actual blueberries. It’s more enjoyable.
You can also drink blueberry juice if you want. There is research showing that blueberry juice improves cognitive function in the elderly.
Besides increasing acetylcholine, wild blueberries also improve brain health by increasing BDNF and improving brain blood flow.
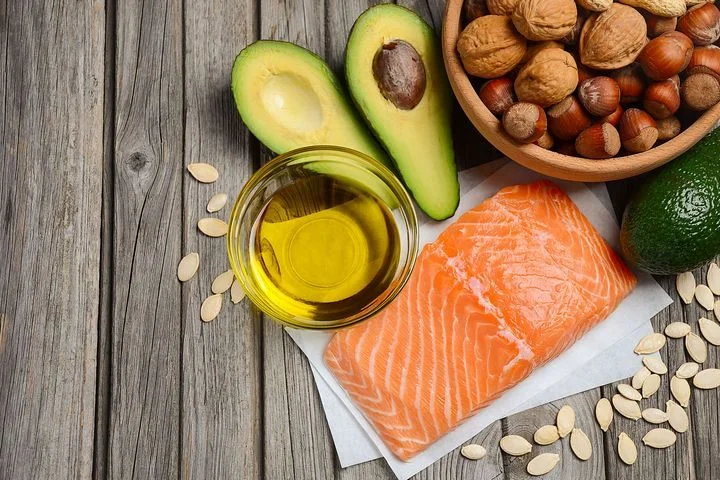
16. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s fatty acids are the highest quality fats for the brain and increasing your intake of them is one of the most impactful actions you can take to promote the normal functioning of your brain and nervous system.
They have been shown in many studies to significantly reduce brain inflammation; improve memory, mood and cognition; and protect against mild cognitive impairment, dementia and Alzheimer's disease.
Research also shows that omega-3 fatty acids increase acetylcholine levels in the brain (34-35).
It’s important to consume enough omega-3 fatty acids because they are essential fats that your body cannot produce itself.
Omega-3 fatty acids are found primarily in cold water fish, including:
Salmon
Black cod
Sablefish
Sardines
Herring
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain Health.
Unfortunately, most people don't consume enough omega-3 fatty acids through their diet.
That’s why I recommend supplementing with krill oil, a special kind of fish oil that contains the essential omega-3 fatty acids.
The Best Herbal Supplements to Increase Acetylcholine in the Brain
There are many different herbs and natural plant compounds that can increase acetylcholine levels.
They usually work by inhibiting acetylcholine esterase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down acetylcholine in the brain.
17. Ginkgo Biloba
Ginkgo Biloba is a plant that has been used in China for thousands of years to treat a number of health problems.
It’s one of the top-selling natural supplements in the world, and it’s even a prescription herb in Germany.
Ginkgo Biloba extract is most commonly used to improve brain health because it increases brain blood flow and improves memory, mood, mental energy, and attention in both healthy and unhealthy individuals.
Ginkgo biloba extract has been shown to enhance cognition by increasing acetylcholine levels in the prefrontal cortex of the brain (42, 45).
In one study, it significantly increased acetylcholine in the hippocampus, which is the area of the brain involved in memory (41).
Another study found that it also inhibits acetylcholine esterase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down acetylcholine. As a result, researchers think it could be used to treat dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (43-44).
Ginkgo Biloba is included in the Optimal Brain supplement.
18. Ginseng
Researchers have found that several types of ginseng significantly reduce the breakdown of acetylcholine (52).
They also increase the synthesis of acetylcholine in the brain, which can reverse memory loss (53).
The best form of ginseng that I have personally benefited the most from is American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolius).
I find that it improves my memory and clears brain fog very quickly.
Research shows that American Ginseng enhances brain function by stimulating the production and release of acetylcholine in the brain (54-55).
One study found it can recover the cognitive function by enhancing acetylcholine levels (56).
19. Huperzine A
Huperzine A is a natural compound found in the Chinese herb Huperzia serrata.
It has neuroprotective effects, and significantly improves cognition in animals and humans (40).
It's been shown to block acetylcholine esterase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down acetylcholine (39).
As a result, it can increase acetylcholine levels in the brain, improving learning and memory (36).
A systematic review concluded it can help reduce cognitive decline and slow down the development of neurodegenerative disorders (38-39).
And in China, it’s approved and prescribed to treat Alzheimer’s disease (37).
20. Bacopa
Bacopa monnieri is a medicinal herb that enhances cognition.
It’s most commonly used to improve memory and reduce symptoms of dementia (48).
Research shows that bacopa blocks the breakdown of acetylcholine and increases the production of acetylcholine (46, 49).
One study found that it can even reverse the memory loss caused by anti-cholinergic drugs (47).
Other studies show that it significantly improves learning and memory by significantly reducing the breakdown of acetylcholine (50-51).
Besides improving memory and cognition, I have found bacopa very relaxing and good at reducing anxiety and stress.
So it’s a good option if you’re looking for something to increase acetylcholine and relieve anxiety at the same time.
21. Gotu Kola
Gotu Kola (Centella asiatica) is a traditional herb with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
It’s been used for centuries in Ayurvedic and traditional Chinese medicine to enhance cognition.
Studies show that it enhances learning and memory by inhibiting the breakdown of acetylcholine in the brain (58-60).
It’s even been shown to reduce the formation of amyloid plaques, which occurs in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease (57).
It's important to point out that the Gotu Kola plant soaks up heavy metals from the soil. So you need to find a high-quality, organic source that doesn’t contain heavy metals.
22. Galantamine
Galantamine is an alkaloid isolated from the plant Galanthus woronowii.
It’s commonly used to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease because it can improve memory, cognitive performance, activities of daily living and behavioral symptoms (62, 64).
Research shows that it maintains acetylcholine levels by slowing down the breakdown of acetylcholine in the brain (61).
It also stimulates acetylcholine activity throughout the entire brain (63).
23. Rhodiola
Rhodiola, also known as golden root or arctic root, is a Traditional Chinese and Scandinavian herb.
It’s one of the most popular adaptogens used to increase physical and mental stamina.
Rhodiola has been shown to improve learning and memory by reducing the breakdown of acetylcholine (65-67).
As a result, researchers think it is a good candidate for the treatment of dementia and other memory disturbances (65).
I personally take this rhodiola supplement. I don't take it every day, only when I need an extra boost in brain function and cognitive energy. It’s especially useful after stressful periods of pushing myself too hard. It helps me recover faster.
Rhodiola also boosts dopamine levels and induces autophagy in the brain.
Be sure to check out this post to learn more about the benefits of rhodiola.
24. Rosemary
Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) is a medicinal plant rich in polyphenols and flavonoids.
It has antidepressant effects by boosting cholinergic activity in brain cells (68).
It also significantly reduces the breakdown of acetylcholine (69).
Researchers found that simply inhaling rosemary essential oil can improve cognitive performance by preventing the breakdown of acetylcholine (70).
Important Hormones That Increase Acetylcholine in the Brain
Hormones levels can also significantly impact your acetylcholine levels. Below are three main hormones that you should optimize.
25. Estrogen
Estrogen is the primary female sex hormone and responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system.
Increasing estrogen levels has been shown to significantly increase the release of acetylcholine in the frontal cortex of the brain (71).
I recommend both men and women get their hormone levels checked regularly, and then optimize them if they want to optimize brain function and feel their best.
You can check your estrogen levels here.
26. Insulin
Insulin is a hormone that significantly affects brain function.
Researchers have found that it passes the blood-brain barrier and acts on insulin receptors directly within the brain.
Unfortunately, many people today develop insulin resistance within the brain.
When this happens, there is a reduction in cognitive function.
So in a new therapeutic approach, commercially-available insulin (Novalin R) is being prepared and added to nasal spray bottles, and sprayed and inhaled through the nose to support the brain and mental health.
Intranasal insulin has been reported to significantly enhance memory, increase mental energy and reduce brain fog.
One possible way it does this is by increasing acetylcholine levels in the brain.
Research shows that insulin improves memory by enhancing cholinergic function and inhibiting the breakdown of acetylcholine in the brain (72).
Intranasal insulin also improves brain blood flow and increases the formation of new synapses in the brain.
If you’re interested in learning more about intranasal insulin, I previously wrote a full article about it. You can read that here.
27. Melatonin
Melatonin is a hormone released by your pineal gland, a small gland in your brain. You can also take it as a supplement.
It helps control your circadian rhythm, and adequate levels of melatonin are necessary to fall asleep quickly and sleep deeply throughout the night.
Research shows that melatonin improves memory by enhancing cholinergic function and inhibiting the breakdown of acetylcholine (73).
This sleep supplement, which contains magnesium and a number of other natural compounds that I’ve used over the years to promote the production of melatonin.
But I work with my clients so that they can naturally produce more melatonin and maximize the quality of their sleep without so many supplements. We have free online workshop that talks about how you can work with us. You can register for the workshop here.
Enjoy This Article? You Might Also Like My FREE Food Guide for Optimal Brain and Mental Health!
References:
(1) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16942753
(2) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18289004
(3) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17184749
(4) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9104933
(5) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15005642
(6) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4061873/
(7) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7958722
(8) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24156263
(9) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23387341
(10) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21195433
(11) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19685700
(12) https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1533210110392944
(13) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1854155/
(14) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2215852
(15) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2215852
(16) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2215852
(17) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2003276
(18) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7752065
(19) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK209058/
(20) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2782876/
(21) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166432808006232
(22) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19056430
(23) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16243721
(24) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0753332216301536
(25) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11245669
(26) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22366543
(27) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16572044
(28) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1393682/pdf/jphysiol01485-0019.pdf
(29) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19576448
(30) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1393682/pdf/jphysiol01485-0019.pdf
(31) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18930076
(32) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29341902
(33) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29339457
(34) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12221201
(35) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9408223
(36) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17056129
(37) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4003111/
(38) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4854009/
(39) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4137276/
(40) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16364207
(41) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17969894
(42) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22784425
(43) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12213536
(44) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21353510
(45) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11090296
(46) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23772955
(47) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21607013
(48) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26413131
(49) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12213536
(50) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16550227
(51) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3746283/
(52) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3659552/
(53) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3659552/
(54) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2952762/
(55) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27112419
(56) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27112419
(57) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3153012/
(58) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3359802/
(59) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17639556
(60) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16214185
(61) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3648782/
(62) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24461047
(63) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4082307/
(64) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20113148
(65) https://www.degruyter.com/view/journals/med/8/2/article-p176.xml
(66) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308814607002439
(68) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23085339
(69) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26059146/
(70) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3736918/
(71) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12020863
(72) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18336929
(73) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18336929
(74) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4011061/
(75) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22664333
(76) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21939673
(77) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22673824
(78) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29163162
(79) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3252552/
(80) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25681529
(81) http://www.scirp.org/journal/PaperInformation.aspx?paperID=19921
(82) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3026477/
(83) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4403272/
(84) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2659740/
(85) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acetylcholine
(86) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1776392
(87) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6431311
(88) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2659740/
(89) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10071091
(90) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10808142
(91) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16183137
(92) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10808142
(93) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16183137
(94) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16183137
(95) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3859808/
(96) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6150928/
(97) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30969605/
(98) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20060422
(99) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4540232/
(100) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1654728
(101) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10071091
(102) https://jnnp.bmj.com/content/66/2/137
(103) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4865532/
(104) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2654795/
(105) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24590577
(106) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3243760/
(107) http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/genpsyneurotransmitters.html
(108) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24590577
(109) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3243760/
(110) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12962529
(110) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12137632
(111) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26942549
(112) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29923184
(113) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14676050
(114) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15888431
(115) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2687934/
(116) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3497293/
(117) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20190638