As someone who has struggled with chronic health problems and has worked hard to overcome them, I’ve tried everything to help improve my symptoms. About five years ago, after receiving some advice from a good friend with celiac disease, I first tried cutting out all wheat products and saw a dramatic difference in my health. In particular, my asthma cleared up for the first time in my life. My lungs opened up and I knew what it felt like to breathe normally.
Read moreHow to Fight Alzheimer's Disease with Intranasal Insulin
Today I want to discuss "intranasal insulin", a cutting-edge therapy that could help a lot of people.
Neurologists and psychiatrists tend to undervalue the impact of hormones originating outside the brain.
Until modern medicine treats the entire body as one unified system, people will continue to lose faith in conventional practitioners and look elsewhere for solutions to their chronic brain and mental health problems.
As Dr. Suzanne Craft, Ph.D, Professor of Gerontology and Geriatric Medicine, explains:
“People are now starting to understand the critical interaction between the brain and the body and that many of the peptides and hormones produced in the body have very substantial roles to play in the brain. I think we’re at the beginning of a very exciting era in which we’re going to be able to start putting together these systems to understand Alzheimer’s disease, which is clearly a disease of the entire organism, not just of the brain.”
Insulin is one of the hormones that significantly affects brain function.
It's been shown to pass the blood-brain barrier and act on insulin receptors directly within the brain (3, 4).
Not only does our body produce and release it, but it can also be taken as a medication, particularly for the treatment of diabetes (1, 2).
Researchers have found that insulin has “neurotrophic, neuromodulatory, and neuroprotective effects” by:
Promoting neuronal growth;
Regulating the levels of certain neurotransmitters;
Increasing brain energy levels (ATP in your mitochondria);
Increasing blood flow in the brain;
Preventing dopaminergic neuron loss;
Protecting against oxidative stress in the brain by restoring antioxidants and energy metabolism (5-13).
“In the brain, insulin has a number of roles to play. It promotes glucose uptake in the neurons of the hippocampal formation and the frontal lobes, areas that are involved in memory. Insulin also strengthens the synaptic connections between brain cells, helping to form new memories. In addition, insulin regulates the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which plays an important role in learning and memory.”
So, it clearly does a lot in the brain, and research shows that it can be therapeutic for a number of mental health conditions, particularly Alzheimer’s disease.
In a new therapeutic approach, commercially-available insulin (Novalin R) is prepared and added to nasal spray bottles, and sprayed and inhaled through the nose to support brain and mental health.
Dr. William Banks, Professor of Internal Medicine and Geriatrics, says there are more than 100 different intranasal compounds that are being tested for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
“Intranasal insulin” is just one of them, and it’s one of the more promising ones, as it’s been reported to significantly enhance memory, increase mental energy, reduce brain fog, improve mood, and lower anxiety and stress levels.
The Link Between Alzheimer’s Disease, Insulin and Diabetes
Many of the brain health experts I’ve talked to are convinced that Alzheimer’s disease should actually be called "Type 3 diabetes".
This is because diabetes and insulin are closely linked to cognitive decline and dementia.
Many studies show that diabetes is associated with an increased risk of cognitive dysfunction, and people with diabetes are 2 to 3 times more likely to be diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment than non-diabetics (14-21).
Researchers have also found that insulin declines in the brain as people age, and patients with Alzheimer’s disease often have insulin resistance and reduced levels of insulin in their brains (25-30)
But what if insulin deficiency is detected in the brain, and then insulin is supplied to the brain, could neurodegeneration and the development of dementia be prevented? And could the progression of existing Alzheimer’s disease be halted?
The answers to these questions appears to be yes:
Diabetic patients who take insulin have improved memory and reduced rates of Alzheimer’s disease;
Elderly diabetics who take insulin have less severe Alzheimer’s disease compared with non-diabetics;
Insulin improves cognition and memory in people with Alzheimer’s disease; and
Insulin prevents and reverses brain degeneration and cognitive impairment in diabetic animals (22-24).
Check out the below video to learn more from one of the leading researchers in the field:
Cutting-Edge Research Shows That Intranasal Insulin Improves Cognition and Memory
The intranasal route of insulin administration provides direct access to the cerebrospinal fluid and brain.
This allows insulin to directly enter the brain from the nose, and bind to receptors within specific areas of the brain that are involved in memory and cognition (42).
“Insulin receptors in the brain are found in high densities in the hippocampus, a region that is fundamentally involved in the acquisition, consolidation, and recollection of new information. ”
An increasing amount of research has been published over the last ten years, demonstrating that intranasal insulin can significantly improve cognition, attention, memory and overall brain function in people with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease (31-33, 38-39, 43-45).
In fact, there are over 30 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials showing that it’s effective at improving memory, learning and cognitive performance in humans (34-37).
Yet most people aren’t aware of it, and doctors aren’t prescribing it, while millions of people suffer from dementia.
One study found that it improved objective biomarkers of neurodegeneration, including amyloid deposits and tau pathology, in people with Alzheimer’s disease within a few months. In the group of patients that didn’t receive intranasal insulin, brain function continued to deteriorate (40).
In another study, researchers gave intranasal insulin to 104 adults with mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer’s disease. At the end of the 4-month study, the participants who received insulin had significantly better memory and cognitive function compared to the group who didn’t receive insulin (41).
The researchers also found that the improvements in cognition were correlated with improvements in objective biomarkers, and concluded that “intranasal insulin therapy can help to stabilize, slow, or possibly even reverse the course of Alzheimer’s disease (41).
Because of the promising research so far, the US government is currently funding a two-year long clinical trial to see if intranasal insulin will help 240 people with Alzheimer’s disease. Results from the Study of Nasal Insulin in the Fight Against Forgetfulness (SNIFF) are expected to be released in 2017.
And intranasal insulin doesn’t just help elderly people with dementia. It’s also been shown to improve memory in younger, healthy individuals (46-51).
Intranasal Insulin and Other Brain and Mental Health Disorders
Alzheimer’s disease isn’t the only brain and mental health condition that can benefit from intranasal insulin.
Here are some others:
ADHD and drug addiction – Insulin affects dopamine, which is a neurotransmitter linked to both these conditions (52).
Depression, anxiety and anger – In one study, 38 healthy people took intranasal insulin for 8 weeks and experienced enhanced mood, increased self-confidence and reduced anger. Another study found that it affected heart-rate variability (53, 59).
Stroke – Researchers point out that “intranasally administered insulin possesses many of the ideal properties for acute stroke neuroprotection” (54, 62).
Bipolar disorder – One study found that intranasal insulin significantly improved executive function in patients with bipolar disorder (55).
Neurodevelopmental disorder – Two studies have found that intranasal insulin improves cognition, autonomy, motor activity, nonverbal communication, social skills and developmental functioning of children and adults with a rare neurodevelopmental disorder (Phelan-McDermid syndrome) (57, 58).
Overall brain function – “Intranasal insulin appears to restore complex neural networking in the direction of normalization”. In other words, it seems to “reboot” the brain (56).
Parkinson’s disease and Down Syndrome – There is no evidence for this yet but there are ongoing trials looking into whether intranasal insulin could help people with these conditions (60, 61).
Safety of Intranasal Insulin and How to Try It Yourself
Numerous studies show that intranasal insulin is incredibly safe and does not cause any significant adverse side effects. The only minor side effects I came across were dizziness, nose bleeding and mild rhinitis, but these were rare (63-65).
This is because unlike regular insulin administration, intranasal insulin only affects the nose and brain. It doesn’t enter the bloodstream, change insulin levels throughout the entire body, or cause low blood sugar (66-83).
Overall, I believe the benefits outweigh the risks and it’s worth trying, especially if you’re struggling with mild cognitive impairment or early Alzheimer’s disease. It may be another decade or more until the research trickles down and reaches your doctor’s office. Research shows that it takes about 17 years for new scientific evidence to be implemented in clinical practice.
However, I’m not a doctor and you should definitely talk to your doctor about this if you’re considering trying it. If you have an open-minded doctor, perhaps they will support you in trying it. Don’t be surprised if they dismiss the idea entirely though.
With that said, you can easily and legally buy insulin yourself. It’s available over the counter without a prescription at any pharmacy (in the US and Canada). Pharmacists hold it behind the counter and you just have to walk up and ask for “Novolin R.” In Canada, it’s called “Novolin Toronto.”
It’s that simple. You don’t need to provide personal identification or sign anything. It costs about $30.
After that, you can get a nasal spray bottle - like this one or this one.
Then, use pliers to carefully remove the rubber cap from the insulin vial, and pour the insulin into the spray bottle.
At this point, you’re ready to use it. Make sure to keep it in the fridge when you're not using it.
Again, I’m not a doctor. So talk to your doctor about this before trying it. But I feel this is worth sharing and writing about considering it has massive potential to help many people who are struggling day-to-day.
Dosage
Each spray from the nasal bottle is 0.1mL or 10IU of insulin.
Dosages in human studies range from 10IU to 160IU (1 to 16 sprays) daily.
In the longest lasting study, participants took either 20 IU (2 sprays) or 40IU (4 sprays) of insulin daily for four months (86).
So, if you’re going to try it, I wouldn’t take more than 40IU (4 sprays) for longer than 4 months.
However, participants in the ongoing SNIFF trial have been taking intranasal insulin for more than one year, so once the results from that study are released in 2017, my recommendation may change.
Overall, self-experimentation is necessary to find the correct dosage that works best for you.
Conclusion
Intranasal insulin is a very impressive and exciting substance, and the lack of side effects is encouraging.
If you’re looking to improve your memory and brain function and avoid Alzheimer’s disease, it’s definitely worth considering and talking to your doctor about it.
All that’s needed is:
Novalin R (US) or Novalin Toronto (Canada)
I’m aware that this might be little bit “out there” for some people, but I think it has the potential to help a lot of people reach optimal brain and mental health.
Please share with anyone who is struggling with cognitive impairment or the early signs of dementia because it isn't a very well known treatment.
References:
(1) http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00125-003-1153-1
(2) http://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/31/11/957.short
(3) http://press.endocrine.org/doi/abs/10.1210/edrv-13-3-387
(4) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26401706
(5) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15750214/
(6) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4191295/
(7) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15750214/
(8) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22586589
(9) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18348871
(10) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23907764
(11) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26040423
(12) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26777890
(13) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4391678/
(14) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4191295/
(15) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22201977/
(18) http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/20/3/438
(19) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11678970
(20) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10647755
(21) http://www.alzheimersanddementia.com/article/S1552-5260(13)02918-X/abstract
(22) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15750215/
(23) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23565496/
(24) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22201977/
(25) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17049785?dopt=Abstract
(26) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17430239/
(27) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16340083/
(28) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4743662/
(29) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18549783
(30) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15750215
(31) http://www.karger.com/Article/Abstract/106378
(32) http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs40263-013-0076-8
(33) http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/1107947
(34) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25008180/
(35) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16266773
(36) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3260944/
(37) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21883804
(38) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22710630?dopt=Abstract
(39) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21911655?dopt=Abstract
(40) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4743662/
(41) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/219116/
(42) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3443484/
(43) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2804944/
(44) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17942819/
(45) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23507773
(46) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20719831/
(47) http://www.psyneuen-journal.com/article/S0306-4530(04)00052-6/abstract
(48) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15288712
(49) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15288712?dopt=Abstract
(50) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19091002?dopt=Abstract
(51) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4391678/
(52) http://www.news-medical.net/news/2007/10/18/31385.aspx
(53) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15288712
(54) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4828994/
(55) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23107220
(56) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25249577
(57) http://www.nature.com/ejhg/journal/v24/n12/full/ejhg2016109a.html
(58) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18948358
(59) http://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/63/12/4083.long
(60) https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02064166
(61) https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02432716
(62) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26040423
(63) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25374101
(64) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18948358
(65) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25374101
(66) http://press.endocrine.org/doi/pdf/10.1210/jc.2007-2606
(67) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4743662/
(68) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4743662/
(69) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23719722?dopt=Abstract
(70) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15288712?dopt=Abstract
(71) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19091002?dopt=Abstract
(72) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26777890
(73) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15288712
(74) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11992114
(75) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26855666
(76) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12951650
(77) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15288712
(78) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2804944/
(79) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12951650
(80) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23107220
(81) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24101698
(82) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25337926
(83) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25374101
(84) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20876713
(85) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15288712
9 Supplements Proven to Help You Overcome Addiction and Withdrawal
I've been dependent on a lot of substances over the years.
When my brain wasn’t working and I struggled with mental illness, it simply made sense to find immediate relief.
I had to rely on substances outside of myself - even if they weren't good for me - until I found better, long-term, sustainable solutions.
I honestly felt like I had no other choice at the time.
And I know there are a lot of people out there grappling with the same problem.
You may feel like you need something to get through the day.
And then something else to fall asleep at night.
Perhaps that’s alcohol, cigarettes, cannabis or harder substances like cocaine, heroin, methamphetamines.
Or maybe you’re on prescription medication, such as antidepressants or benzodazipenes.
And you just have no idea how you could possibly live without these substances.
I’m here to tell you that you can. And you can thrive.
These 9 nutrients, vitamins and supplements have helped me minimize withdrawal symptoms, overcome my addictions, and get on with my life.
I personally have experience with tobacco, nicotine, alcohol, stimulant, benzodiazepines and antidepressant dependence, addiction and withdrawal.
And even if you don’t struggle with addiction, these nutrients are still great for optimal brain function and mental health.
How Does Nutrition And Supplementation Impact Addiction?
Addiction is not simply a psychological issue.
Historically, most drug treatment programs have included counseling and 12-step approaches like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA).
But these traditional approaches are not very effective.
In her book Seven Weeks to Sobriety, Dr. Joan Mathews Larsen points to studies showing that AA has a success rate of about 25 per cent.
This is because they address the psychological aspects of addiction without considering the physical aspects of the disease.
And Dr. Charles Gant worked as the physician and psychiatric consultant for the New York State prison system, and dealt with hundreds of drug users and traffickers.
He realized that they wouldn’t overcome their addictions without addressing their physical health:
“Unless the biochemical imbalances which are the true causes of substance problems are corrected, the benefits of psychological counseling will be marginal for most people.”
Addiction is a chronic brain disease. Studies show that drugs physically change the structure and functioning of the brain, and these documented brain changes lead to cravings (96).
And in my experience and research, high-quality bioavailable nutrients are an important aspect of combating and correcting this.
Research shows that vitamin and mineral deficiencies can cause metabolic imbalances that create addictive cravings (97, 98).
Dr. Roger Williams, an American biochemist who discovered pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), found that rats that were deficient in certain vitamins consumed more alcohol than those that were not vitamin deficient. But once those vitamin deficiencies were fixed, alcohol consumption decreased (99).
Nutritional deficiencies can also cause withdrawal-like symptoms such as fatigue, depression, irritability, and other mental symptoms that block recovery and lead to a relapse.
So, without further ado, let’s get into nutrients and supplements that helped me the most. with my addiction and withdrawal, and explore the research behind them.
1. Citicoline
Citicoline (also known as CDP-Choline) is the most bioavailable form of choline.
Choline is an essential B vitamin that most people don’t consume enough of, because very few foods in the Western diet contain it. That’s why I recommend supplementing with it.
Citicoline has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, and enhances the synthesis of acetylcholine and dopamine, which are two neurotransmitters that are critical for optimal brain function. It also increases the number of acetylcholine and dopamine receptors in your brain (2-7).
Overall, citicoline is one of my favourite supplements for optimal brain function and mental health.
And there’s evidence that it helps reduce addiction to drugs (1).
In one study, people previously addicted to cocaine took 500mg of citicoline twice daily for two weeks and experienced a reduction in cravings for the drug (8).
In another study, people with cocaine dependence and bipolar disorder who supplemented with citicoline reduced their cocaine use. Researchers had directed them to not consume cocaine during the study, and at the end of it, the researchers found less cocaine in the urine of the participants (9).
Some preliminary research also suggests citicoline could help people with alcohol, cannabis and food addiction (10).
It’s important to point out that many prescription drugs are anticholinergic, meaning they reduce acetylcholine in the brain.
The commonly-prescribed antidepressant Wellbutrin is anticholinergic, meaning it inhibits the physiological action of acetylcholine. I took it for multiple years, and I experienced gradual cognitive decline during that time.
Once I got off Wellbutrin, I felt pretty terrible. But once I started supplementing with citicoline, I noticed an improvement in my cognitive function because it increased my levels of acetylcholine and dopamine. I still take it to this day because it helps me focus, improves my mental energy, and clears brain fog.
You can also find some choline in beef liver and egg yolks. That's why I'm a big fan of eating these foods regularly. They’re included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain and Mental Health.
But supplementing with citicoline has a more immediate, noticeable effect.
Citicoline is included in the Optimal Brain supplement.
Make sure you read this article to learn more about the remarkable benefits of Citicoline.
2. Theanine
Theanine is a relaxing amino acid found in tea. It has a number of brain and mental health benefits.
It’s known to produce a calming effect on the brain by crossing the blood-brain barrier and increasing the production of both GABA and dopamine in the brain. Unlike prescription anti-anxiety medication, it does not cause sedation and drowsiness (13, 14, 15).
As I’ve discussed before, theanine can protect your brain from alcohol, increase your brain’s growth hormone, and lower your stress hormones.
Considering all of this, it’s not too surprising that it has anti-addictive properties and can help reduce withdrawal symptoms.
According to the research, it’s particularly helpful when it comes to withdrawal from nicotine and opioids (16, 17).
I find that theanine improves my mood, helps me focus and cancels out the jitters of my morning coffee. It’s sort of like meditation in a pill. My mind has a tendency to jump around a lot, and theanine helps me “zero in” on what I’m doing.
However, too much theanine can also make people anxious. This is because theanine increases alpha brain waves, and I found out that very high alpha brain waves can actually cause anxiety as well. I usually take just 200 mg, but you should experiment and see how much you can tolerate.
You can also get theanine from black and green tea. But there’s usually not enough theanine in them to have a dramatic effect. That’s why I supplement with pure theanine.
Theanine is available in this anti-anxiety supplement, along with a number of other natural compounds that have helped me manage my anxiety over the years.
3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that the body cannot produce itself.
They are found primarily in fish and are necessary for the normal functioning of your brain and nervous system (18).
They can support your mitochondria and increase your brain’s growth hormone, and have been shown to improve mood, sleep, learning and memory. They also protect against psychiatric disorders including depression, mild cognitive impairment, dementia and Alzheimer's disease (19-21).
Considering all this, it’s not too surprising them that omega-3 fatty acids can also help addicts and reduce their withdrawal symptoms.
Research shows that increased anxiety is one of the primary reasons why substance abusers and alcoholics tend to relapse (23, 24).
And one study found that giving omega-3 fatty acids to substance abusers significantly reduced their anxiety (22).
Smokers have lower levels of omega-3 fatty acids, and treatment with fish significantly reduces their level of dependence (25, 28).
Other studies have shown that omega-3 supplements reduce cravings for nicotine and reduce the number of cigarettes people smoke daily (26, 27).
Researchers have also studied the relapse rates of cocaine addicts discharged after a period of detoxification. And they found that the cocaine addicts who relapsed had significantly lower levels of omega-3 fatty acids in comparison to addicts who didn’t relapse (29).
Lastly, in abstinent alcoholics, elevated omega-3 intake reduces stress and cortisol, and omega-3 fatty acids significantly lower the desire for alcohol in mice (30, 31).
“These bipolar mice, like some bipolar patients, love alcohol. The mice on DHA (an omega-3 fatty acid) drank much less; it curtailed their alcohol abusive behavior. There is now substantial evidence at the molecular level that omega-3 fatty acids work on the brain in ways similar to psychiatric drugs.”
Unfortunately, most people don't consume enough omega-3 fatty acids through their diet. That’s why I recommend people supplement with krill oil, a special kind of fish oil that contains the essential omega-3 fatty acids. I find that I have a brighter outlook on life when I take krill oil consistently.
4. Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR)
Acetyl-L-Carnitine (ALCAR) is an acetylated form of the amino acid carnitine.
It has neuroprotective and cognitive-enhancing effects, and as I’ve discussed before, it can support your mitochondria, protect your brain from alcohol, and help you overcome brain fog.
It can also reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
In one study, alcoholic patients treated with ALCAR stayed sober for longer because it reduced their cravings (48).
ALCAR can also help treat opiate addiction and withdrawal.
Thirty subjects with methadone dependence were given 2 grams of ALCAR daily during a 3-week detoxification period, and it reduced their pain and the length of their withdrawal (49).
And research in rats shows that ALCAR can significantly decrease alcohol consumption and reduce the onset of tremors during alcohol withdrawal. Researchers concluded that it should be considered in the treatment of alcohol dependence (50).
ALCAR gives me a huge boost in mental energy and resilience. It sort of feels like drinking a cup of coffee, so it’s helpful if you want to stop or reduce your intake of caffeine.
It's included in the Optimal Brain supplement.
Make sure you read this article to learn more about the remarkable benefits of ALCAR.
5. N-Acetyl-Cysteine (NAC) and/or Glutathione
N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) is a modified form of the amino acid cysteine.
As I’ve discussed before, it can help treat several mental illnesses.
But it can also reduce addiction and cravings during withdrawal (32-34, 41, 42, 45):
In a small study, 13 people abstaining from cocaine were given NAC or placebo over two days. The participants who received NAC witnessed a significant reduction in their withdrawal symptoms and cravings for cocaine. Follow-up studies also showed that NAC reduced desire and interest in cocaine (35-37).
Smokers voluntarily reduced their cigarette use by around 25% after two weeks of supplementing with NAC (38, 39).
Young marijuana users claiming to be addicted to marijuana supplemented with NAC twice daily for four weeks and experienced a significant reduction in their symptoms of addiction (43, 44).
And it’s not just addiction to drugs. NAC also shows promise for the treatment of gambling addiction. A randomized control trial with 27 pathological gamblers showed that gamblers who supplemented with NAC scored 60% lower on the “Obsessive Compulsive Scale for Pathological Gambling." (40).
NAC is also the precursor to glutathione, your body’s master antioxidant, which can help fight addiction.
Chronic use of drugs, such as cocaine, methamphetamine and alcohol, can lead to the formation of oxidative stress (47).
Oxidative stress can change neuronal pathways and cause addictive behaviour. But glutathione can reduce oxidative stress and therefore decrease the development of addiction (46).
NAC is included in Optimal Antiox, along with a number of other antioxidants and nutients that can help you overcome addiction and manage withdrawal.
6. Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that our skin synthesizes when exposed to the sun.
Every tissue in your body has vitamin D receptors, including the brain, heart, muscles, and immune system.
This means your entire body needs it to function properly and a deficiency can lead to costly physiological and psychological consequences, including addiction.
Researchers have concluded that chronic vitamin D deficiency is an environmental factor contributing to drug use. And supplementation should be considered for the effective treatment of drug abuse and addiction (51-54).
Other studies have discovered that:
Vitamin D protects against the dopamine-depleting effects of methamphetamine (52-54);
There is also a positive association between vitamin D deficiency and severity of alcohol-use disorders (55); and
Patients prescribed narcotic pain medication – such as morphine, fentanyl or oxycodone – end up having to take higher doses if they are deficient in vitamin D (56).
I take a Vitamin D supplement every day to optimize my levels.
It's important to test and monitor your Vitamin D levels before and after supplementing with it.
7. Magnesium
Magnesium is a vital mineral that participates in more than 300 biochemical reactions in the body. This includes neurotransmitter and hormonal activity, both of which can have a huge effect on your mood and brain function.
Magnesium is one of the three nutrients that I think everyone should be taking for their brain, as most people are deficient.
The mineral has been shown to decrease dependence on opiates, nicotine, cocaine, amphetamine and alcohol, and reduce the intensity of withdrawal symptoms when stopping these drugs (84).
It can also lower relapse rates, particularly with cocaine and amphetamine addicts (84).
And researchers have concluded that magnesium supplementation can decrease nicotine addiction in heavy smokers.
It does this by naturally improving the stimulation of the reward system, which reduces the need for stimulation by nicotine or by others addictive substances (85).
Studies have also found that magnesium deficiency is very common in people dealing with alcohol addiction and withdrawal. And supplementing with magnesium diminishes withdrawal complications, reduces the severity of their withdrawal symptoms, and lowers their need for anti-anxiety medication (86, 87).
Foods that contain magnesium include spinach, chard, pumpkin seeds, almonds, avocado, dark chocolate and bananas.
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain and Mental Health.
But supplementation or taking Epsom salt baths is still necessary for most people because magnesium is rapidly used up during times of stress and certain psychiatric drugs can deplete magnesium.
Magnesium is included in this supplement.
8. Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral for mental health, especially if you struggle with chronic anxiety.
It can also help treat addiction and withdrawal.
Excessive urinary excretion of zinc and zinc deficiency have been found in drug addicts. And researchers recommend zinc supplementation to treat addiction and reduce withdrawal symptoms (70, 71).
Research shows that opioid users have lower levels of zinc (72-75).
And in the case of alcoholism, alcohol is known to deplete zinc from the body. Over time, chronic alcohol consumption can produce a downward spiral in which zinc deficiency causes chronic stress, driving a person to drink more alcohol, which further depletes zinc and causes more anxiety in the long run.
In animals, zinc reduces the intensity of morphine dependence, and zinc chelators worsen withdrawal symptoms (76, 77, 78).
Some of the best food sources of zinc include oysters, grass-fed beef, pumpkin seeds, cashews, mushrooms and spinach.
These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain and Mental Health.
However, I still recommend at least short-term zinc supplementation to ensure you get enough.
I created and take the Optimal Zinc supplement for that reason.
9. Vitamin C
It might seem unbelievable but there is research demonstrating vitamin C’s usefulness in overcoming addiction and reducing withdrawal symptoms.
First of all, vitamin C levels are significantly lower in drug addicts (68).
And high doses of vitamin C have been shown to increase endorphin levels, decrease opioid use, and reduce the withdrawal syndrome of heroin addicts (58).
The chronic administration of vitamin C can also prevent the development of tolerance and physical dependence on morphine (59, 69).
When I weened off psychiatric medication, I took large doses of vitamin C every day. By large doses, I mean about 10 grams spread throughout the day. I noticed it reduced stress and helped calm me down.
Various studies show that vitamin C reduces stress and anxiety and decreases the severity of depression (62-67).
And other research shows that long-term vitamin C deficiency contributes to nervousness and emotional instability. And there was a 35% reduction in mood disturbance in hospitalized patients after vitamin C treatment (60, 61).
Foods that contain vitamin C include green peppers, citrus fruits, tomatoes, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, broccoli, and cabbage. These foods are included in my Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain and Mental Health.
But it’s best to supplement with it. That way, you know you’re getting enough.
Vitamin C is included in this supplement.
Others
Here are some other nutritional supplements to consider. Based on my research and experience, these nutrients can help manage addiction and withdrawal, but they aren’t as effective as the other ones above and/or there is less research to support their use:
Lithium Orotate (79)
Taurine (80)
B Vitamins (82)
Glutamine (83)
DL-Phenylalanine (DLPA) (81) – I almost included this one in the main list because it has really helped me, but there isn’t too much research on it. I originally wrote about it here.
D-Serine/Sarcosine (88-95)
Conclusion
Just like mental illness, you can beat addiction. They often go hand in hand.
I’ve learned with time, and with the proper information and resources, people can snap out of their addiction cycle and be happy and calm with themselves without mind-altering drugs and habits.
You may feel like you have no other choice, but you do. You can get on with your life without addictive substances.
Overall, I really believe in the power of these nutrients for tackling addiction and minimizing withdrawal symptoms:
Taking a combination of them can make the transition to sobriety much easier.
I’ve experienced the benefits of them firsthand, and I hope you do too.
References:
(1) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23538074
(2) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2695184/
(3) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11796739
(4) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1430829/
(5) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1839138
(6) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1098982
(7) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19351232
(8) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10102764
(9) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17873684
(10) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4139283/
(11) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4011061/
(12) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16055952
(13) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18296328
(14) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21735551
(15) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3560823/
(16) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23233221
(17) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3754842/
(18) http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/71/1/179S.long
(19) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3618203/
(20) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC533861/
(21) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12777162
(22) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18060675
(23) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12414556
(24) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16131851
(25) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26570994
(26) https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/11/141106101903.htm
(27) http://jop.sagepub.com/content/28/8/804
(28) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4804563/
(29) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14500111
(30) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23390041
(31) http://newsinfo.iu.edu/web/page/normal/18785.html
(32) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18440072
(33) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18996163
(34) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18225476
(35) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16449100/
(36) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17606664/
(37) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17113207/
(38) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19103434
(39) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19103434/
(40) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17445781
(41) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19581567
(42) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26975440
(43) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20163391
(44) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24676047
(45) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4009342/
(46) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26809999
(47) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4455547/
(48) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20595193
(49) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18978503
(50) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10761531
(51) http://eneuro.org/content/3/3/ENEURO.0122-15.2016
(52) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2251729413000050
(55) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23916323
(56) https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/03/090320112114.htm
(57) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21448659
(58) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10836211
(59) http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC4166050/
(60) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3727637/
(61) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3599706/
(62) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26353411
(63) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24511708
(64) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3599706/
(65) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12208645
(66) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4376513/
(67) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4376513/
(68) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11641753
(69) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2852062/
(70) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7599515
(71) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4523930/
(72) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11199888
(73) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8886315
(74) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2374368
(75) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6129905
(76) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11068022
(77) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18389791
(78) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4523930/
(79) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3718672
(80) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23392920
(81) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22397264
(82) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9719389
(83) http://hams.cc/glutamine/
(84) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18557129
(85) http://www.omicsonline.org/magnesium-and-zinc-involvement-in-tobacco-addiction-2155-6105.S2-005.pdf
(86) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1844558
(87) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3577989
(88) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21106609
(89) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25801502
(90) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26861675
(91) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4100571/
(92) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23518710
(93) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19595781
(94) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20541592
(95) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22728761
(96) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2851068/
(97) https://www.amazon.com/Food-Behavior-Barbara-Reed-Stitt/dp/0939956098
(98) https://www.amazon.com/Addictions-Nutritional-Approach-John-Finnegan/dp/092742505X
(99) https://www.amazon.ca/Biochemical-Individuality-Roger-Williams/dp/0879838930
13 Powerful Ways to Support Your Thyroid & Mental Health
“When you know better, you do better.”
Sometimes it may feel as if we have no control over our thoughts and emotions. Our minds can take on a life of their own, with no rhyme or reason as to why we're suddenly sad and anxious.
But there are always underlying causes of these mood swings, and with a better understanding of them, you can learn to manage and overcome them.
Like I have, you can connect the dots, determine your underlying triggers, learn to control them and even completely eliminate them over time.
So today I want to talk about thyroid dysfunction. It was one of the underlying issues of my chronic mental illness.
Your thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland located in your neck below your Adam’s apple.
It’s one of your most important glands, producing hormones – thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) – which impact the health and functioning of your entire body.
In fact, normal metabolism and energy levels depend on these hormones.
Your thyroid also plays a key role in the optimal health and functioning of your brain. It can impact your cognition, concentration, mood, memory and emotions.
So when your thyroid hormones are out of balance, you can be too, and brain and mental problems can arise.
Your thyroid can either be overactive and produce too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism), or underactive and produce too little thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism).
Hypothyroidism (low thyroid) is much more common, and since I personally struggled with symptoms of hypothyroidism, this post will mostly focus on that.
Hypothyroidism can also be caused by an autoimmune conditions called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in which the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid tissue.
According to Dr. Datis Kharrazian, author of Why Isn’t My Brain Working? and Why Do I Still Have Thyroid Symptoms?, 90% of people with hypothyroidism have Hashimoto’s.
Here are some of the common brain and mental health symptoms of low thyroid that I experienced:
Chronic fatigue
Brain fog
Low mood
Forgetfulness
Weakness
Sluggishness
Sounds just like depression, doesn’t it?
You Don't Have Mental Illness, You Have Thyroid Problems
Many studies show that people with cognitive, emotional and behavioural disturbances have lower levels of thyroid hormone than the general population, and their psychiatric symptoms improve when they take thyroid hormone.
The following symptoms and disorders have been linked to thyroid problems (69-86):
Depression
Anxiety
Bipolar disorder, mania and mood swings
Irritability and rage
Insomnia
Paranoid schizophrenia and psychosis
Dementia and confusion
Social anxiety disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder
Borderline personality disorder
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
In fact, many people struggling with these conditions see better improvements when they are treated with thyroid hormone than when they are treated with psychiatric medication (and experience fewer side effects).
“Psychiatric patients with subclinical hypothyroidism - especially those with incomplete responses to psychotropic therapy - should usually be treated with thyroid hormone. In some patients with no clear evidence of a biochemical or clinical thyroid disorder, mood symptoms nevertheless respond to thyroid hormone.”
A number of different medical practitioners and researchers have written books about how thyroid problems can negatively affect brain and contribute to mental illness:
“Brain cells have more thyroid hormone receptors than any other tissue, which means that a proper uptake of thyroid hormone is essential for the brain cells to work properly.” – Dr. Barry Durrant-Peatfield, MD, Author of Your Thyroid and How to Keep It Healthy
“How much of what we call “mental illness” is actually thyroid-driven? In my experience, a vast majority.” – Dr. Kelly Brogan, MD, Author of A Mind of Your Own: The Truth About Depression and How Women Can Heal Their Bodies to Reclaim Their Lives
"T3 [thyroid hormone] is actually a bonafide neurotransmitter. If you don’t have enough T3, or if its action is blocked, an entire cascade of neurotransmitter abnormalities may ensue, which can lead to mood and energy changes, including depression and anxiety.”– Dr. Christiane Northrup, MD, Author of Women's Bodies, Women's Wisdom: Creating Physical and Emotional Health and Healing
“Scientists now consider thyroid hormone one of the major players in brain chemistry disorders. And as with any brain chemical disorder, until treated correctly, thyroid hormone imbalance has serious effects on the patient’s emotions and behavior.” – Dr. Ridha Arem, MD, Author of The Thyroid Solution: A Mind Body Program for Beating Depression and Regaining Your Emotional and Physical Health
“There’s a very tight correlation between hypothyroidism and depression. Unfortunately, patients are misdiagnosed with depression when really they have low thyroid. There are well designed clinical trials to show you that your active thyroid hormone is essential to a happy mood. Correcting and nourishing the thyroid gland is absolutely imperative in order to improve mood.” – Suzy Cohen, Author of Thyroid Healthy: Lose Weight, Look Beautiful and Live the Life You Imagine
“People with mental health issues have greater rates of thyroid antibodies and Hashimoto's. I've had so many clients who were misdiagnosed. They were on heavy-duty psychotropic medications. They were hospitalized. But it was their thyroid disorder that was causing their issues.” – Dr. Izabella Wentz, PharmD, Author of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: Lifestyle Interventions for Finding and Treating the Root Cause
So if you struggle with brain or mental illness, you likely do not need a prescription for antidepressants, antipsychotics and anti-anxiety medication. What you really need is to support your thyroid. Treating the underlying thyroid problem is critical to alleviating the associated psychiatric symptoms.
Luckily, there are easy, natural ways for you to do just that.
Below are 13 main strategies I’ve used to balance my thyroid hormones and improve thyroid function.
Before implementing all of them, I highly recommend getting a full thyroid panel so that you know your starting point.
1. Cut Out Gluten
Certain foods can disrupt proper thyroid function and you should avoid them to optimize brain and mental health.
Gluten-containing grains (barley, wheat, rye, spelt) are the worst offenders.
The problem with gluten is that it can increase intestinal permeability (leaky gut syndrome). When this happens, small particles of food can leak into your bloodstream. Your immune system sees these food particles as foreign entities and attacks them, increasing inflammation throughout your body.
On top of this, the molecular structure of gliadin (the protein found in gluten) resembles that of the thyroid gland. So when gliadin enters your bloodstream, your immune system not only attacks the gliadin, but also your thyroid tissue because of its close resemblance. And this can cause many brain and mental health problems (11-13).
Research shows that people with celiac disease and gluten intolerance are more likely to have thyroid diseases and mental illnesses, and vice versa (1-10).
“Many people that have hypothyroidism really have gluten sensitivity. Over time, they actually have significant brain degeneration. When people degenerate their brain, one of the first things they get is depression.”
Thyroid function, and therefore brain and mental health, will often improve after the elimination of gluten-containing grains.
2. Eat Enough Calories and Carbohydrates
Making sure you eat enough calories and carbohydrates on a daily basis is critical for optimal thyroid and brain function.
A landmark paper, known as the Vermont Study, found that thyroid hormone drops when you don’t eat enough calories and carbohydrates (14).
Several other studies also show that ketogenic low-carb diets can suppress thyroid function and reduce thyroid hormone. This is because carbohydrates play a key role on the production of thyroid hormone (15-18).
In previous posts, I have mentioned that fasting and ketogenic dieting can have beneficial effects on your brain. This is still true. However, it's important to note fasting and low-carb diets should be followed intermittently and not consistently over long stretches of time, mainly because of their detrimental effects on the thyroid. I prefer to take exogenous ketones instead. They immediately increase my mental clarity without having to restrict carbohydrates.
My Free Grocery Shopping Guide for Optimal Brain Health contains plenty of healthy, nutrient-dense sources of carbohydrate, including:
Yams
Squash
Potatoes
Carrots
Other root vegetables
Berries
Apples
Bananas
Raw honey
3. Avoid Vegetable Oils
You should also significantly limit all refined vegetable oils, including soybean, corn, safflower, sunflower, and canola.
These oils are predominantly made up of omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), which are highly unstable and oxidize very easily within your body.
Unfortunately, like gluten, rancid PUFAs are everywhere and hard to avoid. Most commercially-prepared processed foods include them.
And your thyroid is particularly vulnerable to their effects.
Dr. Raymond Peat, PhD, says that the sudden increase of fragile and rancid polyunsaturated oils into our food supply after World War II has caused many changes in human health, particularly thyroid function and hormones:
“Their [polyunsaturated oils] best understood effect is their interference with the function of the thyroid gland. Unsaturated oils block thyroid hormone secretion, its movement in the circulatory system, and the response of tissues to the hormone. By 1950, then, it was established that unsaturated fats suppress the metabolic rate, apparently creating hypothyroidism. The more unsaturated the oils are, the more specifically they suppress tissue response to thyroid hormone, and transport of the hormone on the thyroid transport protein. And in 1980, experimenters demonstrated that young rats fed milk containing soy oil incorporated the oil directly into their brain cells, and had structurally abnormal brain cells as a result.”
4. Eat coconut oil
I’ve discussed the brain and mental health benefits of coconut oil before here.
It can help reduce brain fog and enhance your cognitive performance. And it may be accomplishing this by supporting your thyroid.
According to Dr. Raymond Peat, coconut oil is very beneficial to the brain and thyroid:
“Coconut oil has a general pro-thyroid action by diluting and displacing anti-thyroid unsaturated oils. And brain tissue is very rich in complex forms of fats. An experiment in which pregnant mice were given diets containing either coconut oil or unsaturated oil showed that brain development was superior in the young mice whose mothers ate coconut oil. Because coconut oil supports thyroid function, and thyroid governs brain development, including myelination, the result might simply reflect the difference between normal and hypothyroid individuals.”
And you don’t need to stick with coconut oil. Coconut milk, water and meat are other ways to get the benefits of coconut.
5. Try Low-level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is probably the best cutting-edge way to support your thyroid. I wrote about it previously here.
Using it on my thyroid has made a remarkable difference in my energy levels and mental clarity. And this is likely because of an increase in my thyroid hormones.
Multiple studies show that LLLT can improve the production of thyroid hormones and improve thyroid function in patients with chronic autoimmune thyroid disease. Study participants were able to reduce the dosage of their thyroid medication (36, 37).
A study from Brazil showed that LLLT not only reduced the need for thyroid medication in all patients, but 9 months later after the study concluded, it also showed that 47% of patients no longer required any thyroid medication at all. Participants with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis also saw a reduction in their anti-thyroid antibodies by more than 39% (40).
A Russian study also demonstrated a 97% success rate when treating women with subclinical hypothyroidism. Researchers concluded LLLT should be the “method of choice in the treatment of [subclinical hypothyroidism], especially in the elderly” (40).
Animal research has found similar results in rats and rabbits (38, 39).
I shine the Optimal 1000 Brain Photobiomodulation Therapy Light (Combo Red/NIR) device on my thyroid. It includes both red and infrared light. I’m convinced most people would benefit from it.
When I’m travelling, I take this smaller and more convenient device with me.
Infrared saunas are another excellent way to expose yourself to infrared light and support thyroid function. Check out my post about the benefits here.
6. Get Enough Vitamin A and D
Fat soluble vitamins A and D are also critical for optimal thyroid and brain function.
Vitamin D is necessary to help transport thyroid hormone into your cells and deficiency is quite common in people with thyroid problems. Vitamin D deficiency is also associated with thyroid disease and supplementation has been shown to benefit the thyroid. (22-24).
I previously discussed the brain health benefits of vitamin D here.
You should test and monitor your Vitamin D levels regularly.
Vitamin A helps your body produce thyroid hormone and protects the thyroid gland from oxidative stress (which is higher in people with thyroid issues). Research also shows that vitamin A can reduce your risk of hypothyroidism (19-21).
However, I personally don’t recommend you supplement with vitamin A. It’s better to get it from food. Pastured eggs, grass-fed liver and butter (or ghee if you can't tolerate butter) are ideal sources.
Cod liver oil is another great option as it contains both vitamin A, vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids all together. I take it every so often.
7. Get Enough Minerals
Your thyroid gland needs specific trace minerals to do its job properly.
I take and recommend a multi-mineral supplement so that you have all the minerals you need to support brain and thyroid health. It includes a small amount of iodine, selenium, magnesium and zinc.
Iodine is the most important, as it’s one of the building blocks used by your thyroid to create hormones.
However, I don’t recommend supplementing with large doses of iodine separately. Many functional medicine practitioners that I’ve learned from over the years have told me that high iodine intake through supplements can often do more harm than good. Too much supplemental iodine has been shown to cause further thyroid problems (66-68).
So I think the small amount in a multi-mineral is enough.
And getting some more iodine from whole foods, including seafood and sea vegetables, can also benefit you since they contain other nutrients that can support your thyroid.
Selenium is another indispensable mineral for your thyroid and brain health.
It helps regulate and recycle your iodine stores, and selenium-based proteins help regulate thyroid hormone synthesis and metabolism.
Without it, you’ll likely experience low-thyroid symptoms.
Brazil nuts are the richest dietary source of selenium.
Low levels of zinc can also lead to depleted thyroid hormones, and vice versa (34). This is just another reason to supplement with zinc.
As I’ve discussed before, a zinc deficiency can also contribute to stress and anxiety.
And although it isn't mentioned very often, magnesium is also critical for optimal thyroid function. The thyroid gland can't function properly without it (89).
I previously discussed how it can help a lot of people with depression and anxiety here.
8. Reduce Stress and Cortisol
High levels of physical and mental stress can be detrimental to your thyroid function.
Your adrenal glands – two walnut-shaped glands that sit atop the kidneys – secrete your stress stress hormones, such as cortisol, epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Research shows that cortisol inhibits thyroid hormones from getting into your cells, and weakened adrenal glands can lead to hypothyroid symptoms over time (35).
That’s why it’s critical that you manage stress.
I highly recommend you try to do something every day to manage it.
The most effective way to significantly and permanently reduce your stress and anxiety is neurofeedback. It’s advanced, guided meditation and I previously wrote about my experience with it here.
If you can’t access neurofeedback, taking up a daily meditation practice is an excellent idea.
I’m a big fan of the Muse headband . It can guide your meditation. Similar to neurofeedback, it gives you real-time feedback while you meditate. I wrote an entire review about it here, and you can get it through the Muse website.
I also find massage, acupuncture, heart-rate variability (HRV) training and an acupressure mat very helpful as well.
Lying on the acupressure mat while using my EmWave2 for just 10 minutes relaxes my entire body and mind. I do this at night before bed.
Supplements that can help with stress include zinc, ashwagandha and phosphatidylserine, which have been shown to lower cortisol levels (87, 88).
This anti-anxiety supplement also includes a number of natural compounds that have helped me manage my stress over the years.
Lastly, you should get enough sleep and don’t exercise too much. The stress caused by excessive exercise can wear you’re your body and contribute to thyroid problems. So make sure you get plenty of rest and recover between workout sessions.
9. Take Thyroid-Supporting Herbs
A number of different herbs can assist your thyroid gland.
Ashwagandha is one of my favourites. Not only can it reduce stress and anxiety, but a number of studies show that it can boost thyroid hormones (25-29).
Bacopa is another adaptogen that has been shown to increase thyroid (T4) hormone levels by 42% (30).
Forskolin stimulates the release of thyroid hormones (31).
And one study found that ginseng increases and normalizes thyroid hormone levels (32).
And last but not least, researchers say that rhodiola can “improve the quality of life of patients with short-term hypothyroidism” (33).
Rhodiola also has a number of brain and mental health benefits. I explored them previously here.
I’ve experimented with all of these herbs and they have improved my brain and mental health.
But it’s good to know they have some beneficial effects on my thyroid as well.
10. Eat “Head to Tail”
Whole plant foods tend to be much healthier when they’re left whole, as they tend to have various nutrients that work together synergistically.
The same can be said about animal food.
“Muscle meats contain so much tryptophan and cysteine that a pure meat diet can suppress the thyroid. In poor countries, people have generally eaten all parts of the animal, rather than just the muscles – bones, cartilage, skin, organs, and other odd bits. About half of the protein in an animal is collagen, and collagen is deficient in tryptophan and cysteine. This means that, in the whole animal, the amino acid balance is similar to the adult’s requirements.
”
In other words, muscle meat (chicken breasts, lean beef) shouldn’t be your only source of animal protein. Our ancestors didn’t eat this way, so neither should we.
Your body and thyroid prefer and expect to receive a balance of amino acids from different parts of whole animals.
That’s why I recommend “head-to-tail eating” – consuming a wide variety of proteins from the entire animal.
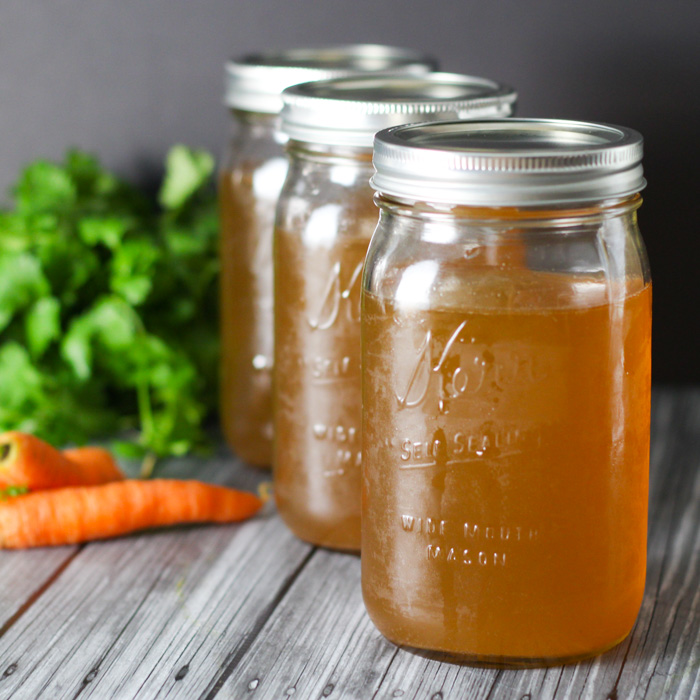
Along with muscle meat, you should regularly cook and eat organ meats such as liver and bone broth.
Bone broth contains collagen, gelatin and amino acids such as glycine and proline that help the body better metabolize muscle meat.
Organ meats such as liver have an abundance of beneficial nutrients that aren’t found in muscle meat alone. For example, it’s much higher in vitamin A, which is important for optimal thyroid health (19, 20).
I previously discussed the benefits of liver in more depth here.
I personally don’t like the taste of liver and bone broth can be inconvenient to make all the time, so I often supplement with grass-fed beef liver capsules and drink high-quality pre-made bone broth.
I also take a Multi-Glandular For Men, which contains a number of different organ tissues. There is also one for women.
But if you’re actually interested in learning about how to cook and incorporate more whole animal proteins into your diet, I recommend checking out the book Odd Bits: How to Cook the Rest of the Animal by Jennifer McLagan.
11. Limit Halogens
Your thyroid doesn’t know the difference between iodine, and other halogens such as bromine, fluorine, chlorine, and perchlorate, which are often found in tap water.
So your thyroid soaks them up and uses them like iodine.
By occupying iodine receptors, they worsen iodine deficiency, inhibit the production of your thyroid hormones and contribute to thyroid dysfunction.
Studies show that chlorine interferes with proper conversion of thyroid hormone (50, 58-61).
That’s why I recommend filtering your drinking and shower water. Brita filters aren't enough because they don’t remove fluoride. I use this water filter to make sure I’m drinking the purest water available. It filters everything out of the water. I also use this filter to remove chlorine from my shower water.
The research shows that bromide in particular can cause a lot of problems. Bromide is found in pesticides, prescription medication, plastic products and personal care products. PBDE (bromide) fire retardants have been added to mattresses, carpeting, electronics, furniture and car interiors since the 1970s.
Even small amounts of bromide can be problematic, depleting iodine and weakening the thyroid gland. Bromide levels are 50 times higher in thyroid cancer than normal thyroid tissue, and elevated levels of bromide have been linked to mental illness, including depression and schizophrenia (50-57).
12. Avoid Environmental and Dietary Mycotoxins
Mycotoxins – toxic metabolites produced by mold – can also disrupt normal thyroid function.
Mycotoxins are released into the air in water-damaged buildings, and you may not realize it’s affecting your brain and thyroid health until you develop certain symptoms. And even then, people frequently won’t make the connection between the mold and their health.
That’s what happened to me, and my hormonal health went downhill, along with my brain and mental health. Luckily I’ve recovered since then.
Mycotoxins are known hormone disruptors that cause inflammation, and a couple of studies mention that there is an increased frequency of “thyroid, immune dysfunction and autoimmune conditions” in people exposed to water-damaged building (41, 42).
And one study shows that mold exposure is correlated with hypothyroidism and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (43).
Kurt and Lee Ann Billings wrote the book Mold: The War Within after extensive personal bouts with toxic mold exposure. They write extensively about their experience and recovery and describe ongoing problems with thyroid dysfunction.
After I moved out of the moldy home, I became extremely sensitive to any environmental mold and mycotoxins.
I now use an air filter in my apartment. It removes any mold spores and smoke that may be in the air.
Low amounts of mycotoxins are often found in some seemingly healthy foods, such as tea, nuts, grains, coffee and chocolate. I recommend finding the freshest, highest-quality, organic versions of these foods.
Lastly, if exposed to mold or their toxins, you should supplement with activated charcoal or bentonite clay.
Activated charcoal and bentonite clay are potent natural treatments that can trap toxins and chemicals, allowing them to be flushed out of your body.
13. Avoid and Remove Other Environmental Toxins
Mold and other halogens aren’t the only endocrine disruptors in your environment that can affect your thyroid metabolism and function.
In the book Thyroid Mind Power, Dr. Karilee Shames reports that “the last 40 years have witnessed a massive increase in the amount of hormone-disrupting synthetic chemicals, finding their way into our air, food and water. The most sensitive and highly susceptible of human tissues turned out to be the thyroid gland.”
Here are some common ones:
Bisphenol A – found in plastic bottles and containers. I recommend you only eat and drink out of glass, ceramic and stainless steel. Avoid storing any of your food in plastic too. BPA-free plastic isn’t much better for you and can still disrupt hormonal health.
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) – found in common household products including non-stick cookware and waterproof fabrics. Researchers have found that people with higher levels of PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) have a higher incidence of thyroid disease (44, 45).
Other pesticides and chemical additives – You should avoid processed food and eat organic as often as possible, wash all produce thoroughly to minimize your pesticide exposure, and find personal care products that don’t include toxic chemicals.
I also recommend increasing your levels of glutathione – your body’s main antioxidant and master detoxifier – to help your body combat the above substances from your body. I do this by supplementing with glutathione on regular basis.
Or you could take NAC and Vitamin C to help your body produce more of its own glutathione.
Researchers have found that a decrease in thyroid function could be reversed by NAC supplementation, which increased glutathione. This is because glutathione plays a key role in the production and conversion of your thyroid hormones (46-49).
Epsom salt baths, infrared saunas, and turmeric can also help your body release and remove environmental toxins.
Summary and Conclusion
With the right information, you can make simple choices to improve thyroid health.
Here's a summary of everything we've gone over:
Cut out gluten-containing grains (barley, wheat, rye, spelt)
Don't follow a long-term ketogenic low-carb diet and eat enough calories and healthy sources of carbohydrates. See my free food guide for plenty of options. And consider taking exogenous ketones to get the cognitive benefits of a ketogenic diet without actually having to follow the diet.
Avoid refined vegetable oils, including soybean, corn, safflower, sunflower, and canola
Eat coconut oil
Supplement with Vitamin D, and make sure you get enough Vitamin A from egg yolks, grass-fed liver and ghee
Take a multimineral with iodine, selenium and zinc
Reduce stress with deep sleep, massage, acupuncture, meditation, neurofeedback, the Muse headband, an acupressure mat, the EmWave2, ashwagandha and phosphatidylserine
Take herbs such as bacopa, ginseng, forskolin and rhodiola
Eat beef liver and bone broth
Filter your drinking water with a filtration system to avoid fluoride, chlorine and other halogens
Avoid mold, mycotoxins and other environmental toxins, and protect yourself from them with an air filter, activated charcoal and glutathione
So with that, I want to leave you with a quote from a book I read recently by Sam Harris, called Free Will.
I think this quote is appropriate considering the wide variety of factors that underlie brain and mental health problems:
“Becoming sensitive to the background causes of one’s thoughts and feelings can - paradoxically - allow for greater creative control over one’s life. It is one thing to bicker with your wife because you are in a bad mood; it is another to realize that your mood and behaviour have been caused by low blood sugar. This understanding reveals you to be a biochemical puppet, of course, but it also allows you to grab hold of one of your strings: A bite of food may be all your personality requires. Getting behind our conscious thoughts and feelings can allow us to steer a more intelligent course through our lives (while knowing, of course, that we are ultimately being steered).”
So even though it seems like there are an overwhelming amount of “strings” to pull, realize that you don’t have to pull them all at once.
You just have to start with one, and go from there.
And then over time, you'll start to get a handle on all of them, and you'll heal.
References:
(1) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11280546
(2) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12217453
(3) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11123714
(4) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10529537
(5) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2111403/
(6) http://www.eje-online.org/content/130/2/137.abstract
(7) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15244201
(8) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9872614
(9) http://www.ncbi.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12919165lm.nih.gov/pubmed/12919165
(10) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11768252
(11) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12366374
(12) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19014325
(13) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1808742/
(14) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC371281/
(15) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6761185
(16) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3740086
(17) http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/35/1/24.full.pdf
(18) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1249190
(19) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6470830
(20) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23378454
(21) http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/34/8/1489.abstract
(22) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3921055/
(23) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12919165
(24) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10750047
(25) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19789214
(27) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1211/146080800128735782/abstract
(28) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9811169
(29) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10619390
(30) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S037887410200048X
(31) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6327383
(32) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6327383
(33) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20946017
(34) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3746228/
(35) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17002934
(36) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20662037
(37) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22718472
(38) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25265487
(39) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25975382
(40) http://valtsus.blogspohttp://va
(41) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3654247/
(42) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15143854
(43) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/430949
(44) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24407430
(45) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2866686/
(46) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21540553?dopt=Abstract
(48) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7408784
(49) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7052928
(50) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8909694
(51) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15255296
(52) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10999431
(53) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9542578
(54) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9341949
(55) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8909694
(56) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6548284
(57) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8909694
(58) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3890436/
(59) http://www .ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1087230
(60) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19318504
(61) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3956646/
(62) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9140329
(63) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21001996
(64) www.gulflink.osd.mil/library/randrep/pb_paper/mr1018.2chap10.html
(65) http://www.optimox.com/iodine-study-18
(66) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7477223
(67) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20517655?dopt=AbstractPlus
(68) http://www.eymj.org/Synapse/Data/PDFData/0069YMJ/ymj-44-227.pdf
(69) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15213796
(70) http://www.drrichardhall.com/Articles/hashimoto.pdf
(71) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11958781
(72) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17141745
(73) http://bmcpsychiatry.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-244X-4-25
(74) http://cpementalhealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1745-0179-1-23
(75) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19215985
(76) http://www.ccjm.org/indhttp://www.ccjm.org/index.php?id=107937&tx_ttnews[
(77) http://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/thyroid-deficiency-and-mental-health
(78) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20404728
(79) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27268005
(80) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24480318
(81) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24480318
(82) http://www.eje-online.org/content/138/1/1.full.pdf
(83) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24443228
(84) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24345793
(85) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3013313/
(86) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23380316
(87) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23439798
(88) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1325348